| Kinase Assay: |
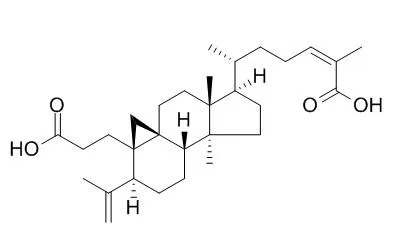
| Nat Prod Res. 2015 Jan 6:1-7. | | Synthesis and biological evaluation of nigranoic acid esters as novel human neutrophil elastase inhibitors.[Pubmed: 25560928] | Human neutrophil elastase (HNE) has been implicated as a major contributor in the pathogenesis of diseases, such as lung disorders and other inflammatory diseases.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A series of 12 new Nigranoic acid esters were regioselectively synthesised in good yields and evaluated for HNE inhibitory activity. Nigranoic acid exhibited significant inhibitory activity against HNE with the IC50 value of 3.77 μM, and six esters displayed considerable inhibitory effects on HNE with IC50 values in the range of 2.61-8.95 μM.
CONCLUSIONS:
The Nigranoic acid esters having phenyls substituted with bromine and trimethoxyls (3h and 3b) showed stronger inhibitory activity on HNE than Nigranoic acid. |
|
| Cell Research: |
| J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 May 14;153(3):725-31. | | Effect of nigranoic acid on Ca²⁺ influx and its downstream signal mechanism in NGF-differentiated PC12 cells.[Pubmed: 24674947] | Schisandra chinensis has a long history of use as a famous traditional Chinese medicine. The plants of genus Schisandra, especially Schisandra neglecta, Schisandra rubriflora, and Schisandra sphaerandra are used in the same way as Schisandra chinensis in the folk medicine to treat insomnia, fatigue, increasing intelligence, and tranquilizing. Many studies showed that lignans were the major active components of Schisandra genus, whereas the bioactivity of abundant triterpenoids in Schisandra genus, such as Nigranoic acid (SBB1, 3,4-secocycloartene triterpenoid), has not been examined yet in neuropathology.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
After treating with Nigranoic acid, intracellular Ca(2+) concentration was analyzed by Ca(2+) fluorescent indicator (Fluo-4 AM) in NGF-differentiated PC12 cells. Intracellular nitric oxide (NO) level was analyzed using NO fluorescent indicator (DAF-FM). The expression of extracellular signal regulated kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) was analyzed by western blotting, and the temporal mRNA for BDNF and c-fos was analyzed using reverse transcription quantitative PCR. We found that Nigranoic acid induced Ca(2+) influx in a time- and concentration-dependent manner, which was significantly attenuated in Ca(2+) free media. Nigranoic acid promoted the intracellular NO production which depended on increasing cytoplasmic Ca(2+) level. Moreover, Nigranoic acid stimulated activation of ERK1/2 through Ca(2+)-CaMKII pathway. In addition, we found that Nigranoic acid increased the expression of BDNF and c-fos mRNA.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Nigranoic acid is able to promote NO production and stimulate phosphorylation of ERK1/2 through Ca(2+) influx, further impact expression of BDNF and c-fos, which provides evidence for the effects of Nigranoic acid that may be benefit to enhance mental and intellectual functions. |
|
| Animal Research: |
| Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015 Jan;71(1):345-51. | | Protective effects of nigranoic acid on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and its mechanism involving apoptotic signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 25168103] | The goal of this study was to assess the expression of poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) and apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) in the hippocampal CA1 region, and to find out whether Nigranoic acid treatment exhibits protective effects on brain through PARP/AIF signaling pathway in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion animal model.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Rats were randomly divided into three groups: Sham-surgery, ischemia-reperfusion, and Nigranoic acid-treated. Rat models of middle cerebral artery occlusion were prepared using a way of thread occlusion. Rats in the Nigranoic acid group were administered with 1 mg/kg intragastric Nigranoic acid 6 and 2 h before brain ischemia, respectively. Following reperfusion, samples were collected at different time-points (6, 24, and 72 h) and each group was further divided into three subgroups. Apoptosis was measured using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl-transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling method. The protein expression levels of AIF and PARP were detected using Western blot and AIF mRNA quantity was evaluated using the reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Apoptosis, levels of AIF and PARP protein expression, and levels of AIF mRNA expression were significantly increased in the ischemia-reperfusion group compared with the sham-surgery group. However, apoptosis and the expression levels of AIF protein, PARP protein, and AIF mRNA at different time-points were significantly decreased in the Nigranoic acid-treated group compared with the model group.
CONCLUSIONS:
We can judge that Nigranoic acid has a strong protective effect on rat cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, and acts by downregulating nerve cell apoptosis by preventing the overactivation of PARP and AIF nuclear translocation. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)