| In vitro: |
| 《Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs》 2014-01 | | Alkaloids from Zuojin Formula and their cytotoxicities against proliferation of cancer cells[Reference: WebLink] | To study the alkaloid constituents of Zuojin Formula, consisting of Coptidis Rhizoma and Euodiae Fructus, and to evaluate their cytotoxicities against the proliferation of cancer cells in human digestive tract.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
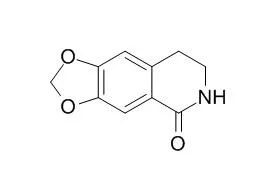
The constituents were isolated and purified by column chromatography on silica gel and Sephadex LH-20, as well as the chemical structures of alkaloids were determined by physicochemical properties and spectral data analyses. The cytotoxicities assay against human gastric NCI-N87 and colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cell lines was carried out by MTT method. Fifteen alkaloids were obtained from the normal butanol soluble fraction of 70% ethanolic extract in Zuojin Formula and identified as rutaecarpine(1), evodiamine(2), rhetsinine(3), coptisine(4), wuchuyuamide III(5), 8-trichloromethyl-7, 8-dihydropalmatine(6), epiberberine(7), 8-trichloromethyl-7, 8-dihydroepiberberine(8), 8-trichloromethyl-7, 8-dihydrocoptisine(9), palmatine(10), berberine(11), 1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydro-1-oxo-β-carboline(12), Noroxyhydrastinine(13), 8-oxo-epiberberine(14), and corydaldine(15). Compounds 1, 2, 4, and 11 showed the inhibitory activities against the proliferation of NCI-N87 and Caco-2 cell with the half inhibitory concentration of 12.61—91.18 μmol/L.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compound 8 is a new compound. Compounds 1, 2, 4, and 11 may be the main effective components in Zuojin Formula against the proliferation of cancer cells in human digestive tract. | | Chem Biodivers. 2017 Jul;14(7). | | Melanogenesis-Inhibitory and Cytotoxic Activities of Limonoids, Alkaloids, and Phenolic Compounds from Phellodendron amurense Bark.[Pubmed: 28425165] | Four limonoids, 1 - 4, five alkaloids, 5 - 9, and four phenolic compounds, 10 - 13, were isolated from a MeOH extract of the bark of Phellodendron amurense (Rutaceae). Among these, compound 13 was new, and its structure was established as rel-(1R,2R,3R)-5-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-1-(methoxycarbonylmethyl)indane-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (γ-di(methyl ferulate)) based on the spectrometric analysis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Upon evaluation of compounds 1 - 13 against the melanogenesis in the B16 melanoma cells induced with α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), four compounds, limonin (1), Noroxyhydrastinine (6), haplopine (7), and 4-methoxy-1-methylquinolin-2(1H)-one (8), exhibited potent melanogenesis-inhibitory activities with almost no toxicity to the cells. Western blot analysis revealed that compound 6 inhibited melanogenesis, at least in part, by inhibiting the expression of protein levels of tyrosinase, TRP-1, and TRP-2 in α-MSH-stimulated B16 melanoma cells. In addition, when compounds 1 - 13 were evaluated for their cytotoxic activities against leukemia (HL60), lung (A549), duodenum (AZ521), and breast (SK-BR-3) cancer cell lines, five compounds, berberine (5), 8, canthin-6-one (9), α-di-(methyl ferulate) (12), and 13, exhibited cytotoxicities against one or more cancer cell lines with IC50 values in the range of 2.6 - 90.0 μm. In particular, compound 5 exhibited strong cytotoxicity against AZ521 (IC50 2.6 μm) which was superior to that of the reference cisplatin (IC50 9.5 μm). |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)