| Kinase Assay: |
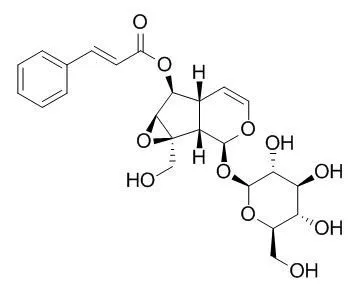
| Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 7;44(1):180-3. | | Picroliv, picroside-I and kutkoside from Picrorhiza kurrooa are scavengers of superoxide anions.[Pubmed: 1321626] | Picroliv, the active principle of Picrorhiza kurrooa, and its main components which are a mixture of the iridoid glycosides, Picroside I and kutkoside, were studied in vitro as potential scavengers of oxygen free radicals.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The superoxide (O2-) anions generated in a xanthine-xanthine oxidase system, as measured in terms of uric acid formed and the reduction of nitroblue tetrazolium were shown to be suppressed by picroliv, Picroside I and kutkoside. Picroliv as well as both glycosides inhibited the non-enzymic generation of O2- anions in a phenazine methosulphate NADH system. Malonaldehyde (MDA) generation in rat liver microsomes as stimulated by both the ascorbate-Fe2+ and NADPH-ADP-Fe2+ systems was shown to be inhibited by the Picroliv glycosides. Known antioxidants tocopherol (vitamin E) and butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) were also compared with regard to their antioxidant actions in the above system. It was found that BHA afforded protection against ascorbate-Fe(2+)-induced MDA formation in microsomes but did not interfere with enzymic or non-enzymic O2- anion generation; and tocopherol inhibited lipid peroxidation in microsomes by both prooxidant systems and the generation of O2- anions in the non-enzymic system but did not interfere with xanthine oxidase activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present study shows that picroliv, Picroside I and kutkoside possess the properties of antioxidants which appear to be mediated through activity like that of superoxide dismutase, metal ion chelators and xanthine oxidase inhibitors. |
|
| Cell Research: |
| Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 6(1):49-58. | | Iridoid glycosides-Kutkin, Picroside I, and Kutkoside from Picrorrhiza kurroa Benth inhibits the invasion and migration of MCF-7 breast cancer cells through the down regulation of matrix metalloproteinases 1st Cancer Update[Reference: WebLink] | Aim of the study Here, MCF-7 cell lines (Human breast cancer) were used to test whether P. kurroa extract (PE) and its isolated iridoid glycosides Picroside I (PS), Kutkoside (KS), and Kutkin (KT) exerts the anti-invasion activity via down-regulation of the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). MMPs play an important role in solid tumor invasion and migration.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The activity and expression of gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) and collagenases (MMP-1 and MMP-13), protein, and mRNA were detected by gelatin zymography, and RT-PCR. The migratory and invasive capacities of MCF-7 cell lines were measured by the wound scratch migration assay. The preliminary cytotoxicity testing was done by MTT assay and propidium iodide staining. Further the inhibition of inflammatory mediators was also done by quantification of nitrite inflammatory mediators.
The study showed that PE and its isolated iridoids glycosides PS, KS, and KT exhibited considerable cytotoxic potential in a dose-dependent manner. Further PE, PS, KS, and KT inhibited MCF-7 cell invasion and migration, and decreased MMP-2, 9 and MMP-1, 13 activities. Furthermore, PS, KS, and KT reduced MMPs expression at protein and mRNA levels, and suppression of the inflammatory mediators was also exhibited.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggest that PS, KS, and KT may be the valuable anti-invasive drug candidates for cancer therapy by suppressing Collagenases and Gelatinases. PS, KS, and KT showed good results in comparison with PE. PS and KS exhibit almost comparable down regulation while KT exhibited maximum suppression of invasion, migration, and expression of MMPs. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
| Phytochem Anal. 2013 Nov-Dec;24(6):598-602. | | A proposed biosynthetic pathway of picrosides linked through the detection of biochemical intermediates in the endangered medicinal herb Picrorhiza kurroa.[Pubmed: 23696248] | Picrorhiza kurroa Royle ex Benth is an important medicinal herb used in the preparation of several herbal drug formulations due to the presence of Picroside I (P-I) and picroside-II (P-II) along with other iridoid-glucosides derivatives.
The endangered status of P. kurroa coupled with lack of information on biosynthesis of Picroside Iand P-II necessitate deciphering the biosynthetic pathway for picrosides.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
LC with electrospray ionisation (ESI) and quadrupole time of flight combined with MS/MS was used to detect intermediates and assemble the picrosides biosynthetic pathway in P. kurroa. The presence of catalpol and aucubin, the major backbone structures of picrosides, along with intermediate metabolites boschnaloside, bartsioside and mussaenosidic acid, was confirmed in ESI negative mode with pseudomolecular ion peaks, that is, m/z 361, m/z 343, m/z 345, m/z 329 and m/z 375 ions and their fragmentation patterns.
CONCLUSIONS:
The picrosides biosynthetic pathway is expected to provide a reliable platform towards understanding the molecular components (genes/enzymes) of Picroside I and P-II biosynthesis in P. kurroa for their eventual utilisation in various applications. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)