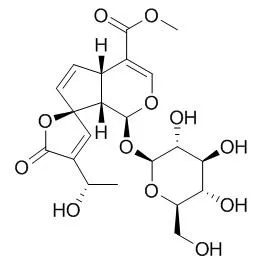
| Animal Research: |
| Phytomedicine. 2004 Feb;11(2-3):169-74. | | Effects of plumieride, an iridoid on spermatogenesis in male albino rats.[Pubmed: 15070168 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Oral feeding of male rats with Plumieride (15 mg/rat/day) for the period of 60 days did not cause any significant change in the body weight of treated rats. However, the weights of testes, epididymides, seminal vesicle and ventral prostate were significantly reduced when compared to control values. The production of step-19 spermatids was reduced by 87.26% in Plumieride treated rats. The population of preleptotene and pachytene spermatocytes were decreased by 64.26% and 55.13% respectively. Spermatogonia and sertoli cell population was also affected. Plumieride treatment resulted in an arrest of spermatogenesis without any systemic side effect. Sperm motility as well as sperm density was reduced significantly. The number of mature Leydig cells was decreased and complete suppression of fertility was observed. A significant fall in the protein and sialic acid contents of the testes, epididymides, seminal vesicle and ventral prostate as well as glycogen content of testes was also noticed. Fructose in seminal vesicle was lowered whereas testicular cholesterol was elevated. There was no significant change in RBC and WBC count, haemoglobin, haematocrit and sugar in the whole blood and total protein, cholesterol, phospholipid and triglycerides in the serum.
CONCLUSIONS:
Plumieride administration arrests spermatogenesis in male rats without noticeable side effects. For the clinical use more experiments should be carried out in a phased programme. | | Antioxidants (Basel). 2014 Nov 27;3(4):798-813. | | Antioxidant Potential of Plumieride against CCl₄-Induced Peroxidative Damage in Rats.[Pubmed: 26785241] |
In search of a new potent as an antioxidant from natural sources, Plumieride-an iridoid isolated from the methanol extract of the bark of Plumeria bicolor (family Apocynaceae) was evaluated for its antioxidant potential against CCl₄-induced peroxidative damage in liver of rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antioxidant potential was evaluated by using hepatic tissue for SOD (superoxide dismutase), CAT (catalase), GSH (reduced glutathione), GPx (glutathione peroxidase), GR (glutathione reductase) and LPO (lipid peroxidation) alongwith the concomitant blood serum for AST & ALT (aspartate and alanine transaminases), GGT (gamma glutamyl transpeptidase), ALP (alkaline phosphatase), total bilirubin and total protein contents. All the biochemical parameters were significantly (p ≤ 0.001) altered by CCl₄ (0.3 mL/kg body weight/twice a week, intra-peritoneally for 30 days). Simultaneously, oral treatment with Plumieride (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg body weight/day for 30 days), restored all the parameters towards a normal level, remarkably. The histological findings of liver sections further corroborated the antioxidant potential of Plumieride compared with standard drug-silymarin.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, Plumieride consists of sugar molecules, which have alcoholic groups. Therefore, the alcoholic groups of sugar increase its antioxidant potential through intermolecular hydrogen bonding along with the thiol(SH) group of non-protein thiols and enzymes resulting in the restoration of the antioxidant system. Therefore, it might be considered a natural antioxidant against peroxidative damage in rats. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)