| In vitro: |
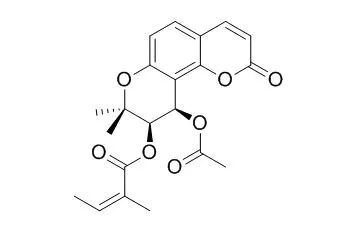
| Bioorg Med Chem. 2006 Nov 1;14(21):7138-45. | | (+/-)-3'-O, 4'-O-dicynnamoyl-cis-khellactone, a derivative of (+/-)-praeruptorin A, reverses P-glycoprotein mediated multidrug resistance in cancer cells.[Pubmed: 16875827] | P-glycoprotein (Pgp) is an ATP-driven membrane exporter for a broad spectrum of hydrophobic xenobiotics. Pgp-overexpression is a common cause of multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer cells and could lead to chemotherapeutic failure.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Through an extensive herbal drug screening program we previously showed that (+)-praeruptorin A/(-)-Praeruptorin A (PA), a naturally existing pyranocumarin isolated from the dried root of Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn., re-sensitizes Pgp-mediated MDR (Pgp-MDR) cancer cells to cancer drugs. A number of PA derivatives were synthesized and one of these, (+/-)-3'-O, 4'-O-dicynnamoyl-cis-khellactone (DCK), was more potent than PA or verapamil in the reversal of Pgp-MDR. In Pgp-MDR cells DCK increased cellular accumulation of doxorubicin without affecting the expression level of Pgp. In Pgp-enriched membrane fractions DCK moderately stimulated basal Pgp-ATPase activity, suggesting some transport substrate-like function. However, DCK also inhibited Pgp-ATPase activity stimulated by the standard substrates verapamil or progesterone with decreased V(max)s but K(m)s were relatively unchanged, suggesting a primarily non-competitive mode of inhibition. While the binding of substrates to active Pgp would increase the reactivity of the Pgp-specific antibody UIC2, DCK decreased UIC2 reactivity.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that DCK could bind simultaneously with substrates to Pgp but perhaps at an allosteric site and thus affect Pgp-substrate interactions. | | Chem Biol Interact. 2010 Jul 30;186(2):239-46. | | (+/-)-Praeruptorin A enantiomers exert distinct relaxant effects on isolated rat aorta rings dependent on endothelium and nitric oxide synthesis.[Pubmed: 20433815 ] | Praeruptorin A is a coumarin compound naturally occurring in the roots of Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn., a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of certain respiratory diseases and hypertension. Although previous studies indicated the relaxant effects of (+/-)-praeruptorin A on tracheal and arterial preparations, little is known about the functional characteristics of the enantiomers.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, the two enantiomers were successfully isolated and identified by using a preparative Daicel Chiralpak AD-H column, and their relaxant effects on aorta rings were observed and compared. (+)-Praeruptorin A showed more potent relaxation than (-)-Praeruptorin A against KCl- and phenylephrine-induced contraction of rat isolated aortic rings with intact endothelium. Removal of the endothelium remarkably reduced the relaxant effect of (+)-praeruptorin A but not that of (-)-Praeruptorin A. Pretreatment of aortic rings with N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase) or methylene blue (MB, a soluble guanylyl cyclase inhibitor) resulted in similar changes of the relaxant effects of the two enantiomers to endothelium removal. Molecular docking studies also demonstrated that (+)-praeruptorin A was in more agreement to nitric oxide synthase pharmacophores than (-)-Praeruptorin A. On the other hand, the two enantiomers of praeruptorin A could slightly attenuate the contraction of rat aortic rings induced by internal Ca(2+) release from sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR).
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings indicated that (+)-praeruptorin A and (-)-Praeruptorin A exerted distinct relaxant effects on isolated rat aorta rings, which might be mainly attributed to nitric oxide synthesis catalyzed by endothelial nitric oxide synthase. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)