| In vitro: |
| Molecules. 2016 Apr 22;21(4):528. | | Enantioselective Separation of 4,8-DHT and Phytotoxicity of the Enantiomers on Various Plant Species.[Pubmed: 27110760 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
As a candidate for bioherbicide, 4,8-dihydroxy-1-tetralone (4,8-DHT) was isolated from Caryospora callicarpa epicarp and its two enantiomers, S-(+)-isosclerone and R-(-)-Regiolone, were separated by chiral high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) on a Chiralcel OD column with chiral stationary phase (CSP)-coated cellulose-tris(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate). Then, the phytotoxicity of 4,8-DHT and its enantiomers toward the seeds germination and seedling growth of the five tested plant species, including lettuce (Latuca sativa), radish (Raphanus sativus), cucumber (Cucumis sativus), onion (Allium cepa), and wheat (Triticum aestivum), were investigated and the results indicated a hormesis at low concentration of 4,8-DHT and its enantiomers, but a retardant effect at high concentration.
CONCLUSIONS:
Between the two enantiomers of 4,8-DHT, the S-(+)-isosclerone was more toxic to seeds germination and seedling growth of the five tested plant species than the R-(-)-Regiolone, and also the phytotoxicity of S-(+)-isosclerone varied with different plants. For example, S-(+)-isosclerone was the most active to seedling growth of lettuce, indicating that S-(+)-isosclerone had specific effects on different organisms.Thus, all of the chirality and concentration of 4,8-DHT, as well as the affected plant species, need to be taken into consideration in the development and utilization of 4,8-DHT. | | Cell Prolif. 2014 Apr;47(2):172-9. | | Anti-proliferative and apoptotic activities of constituents of chloroform extract of Juglans regia leaves.[Pubmed: 24467376] | To evaluate anti-proliferative as well as apoptotic activities of compounds identified in chloroform extract of Juglans regia leaves, on human breast and oral cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and BHY).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Column chromatography, MTT assay, flowcytometry and western blotting have all been used in the study. Bioassay-guided fractionation of chloroform extract of J. regia afforded isolation of 5-hydroxy-3,7,4'-trimethoxyflavone [1], lupeol [2], daucosterol [3], 4-hydroxy-α-tetralone [4], β-sitosterol [5], 5,7- dihydroxy-3,4'-dimethoxyflavone [6] and Regiolone [7]. Structures of the compounds were established on the basis of spectroscopic analyses [Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass]. All compounds inhibited proliferation of MCF-7 (human breast adenocarcinoma) and BHY (human oral squamous carcinoma) cells in a concentration-dependent manner. Compounds 6 and 7 had potent cytotoxic effects on both MCF-7 and BHY cells (IC50 21-51 μm), yet were not toxic to normal cells. MCF-7 growth inhibition was attributed to apoptosis; population of apoptotic cells increased from 1.12% in controls to 5.64 and 8.1% after 48-h treatment with compounds 6 and 7, indicating their potential at inducing early and late apoptosis. The caspase cascade was not activated, as indicated by only insignificant cleavage of caspase-3.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggest that compounds 6 and 7 can induce apoptosis in MCF-7 cells through the caspase-3 independent pathway. | | J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Sep 14;59(17):9201-6. | | Botrytone, a new naphthalenone pentaketide produced by Botrytis fabae, the causal agent of chocolate spot disease on Vicia faba.[Pubmed: 21780794 ] | A strain of Botrytis fabae isolated from faba bean (Vicia faba L.) plants displaying clear chocolate spot disease symptoms produced phytotoxic metabolites in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
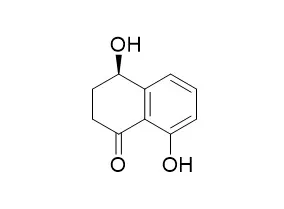
The phytotoxins isolated from the culture filtrate organic extract were characterized by spectroscopic and optical methods. A new naphthalenone pentaketide, named botrytone, was isolated and characterized as (4R)-3,4-dihydro-4,5,8-trihydroxy-1(2H)-naphthalenone together with other well-known closely related naphthalenones such as Regiolone and cis- and trans-3,4-dihydro-2,4,8-trihydroxynaphthalen-1(2H)-ones.
When tested on leaves of the host plant, with the cis- and trans-3,4-dihydro-2,4,8-trihydroxynaphthalen-1(2H)-ones assayed in mixture, Regiolone demonstrated the highest level of phytotoxicity together with cis- and trans-3,4-dihydro-2,4,8-trihydroxynaphthalen-1(2H)-ones.
CONCLUSIONS:
Botrytone showed moderate phytotoxic activity at 1 mg/mL and was still phytotoxic at 0.5 mg/mL. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)