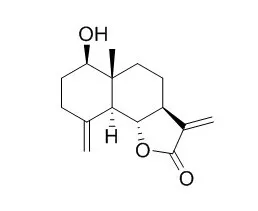
| In vitro: |
| Brain Res. 2013 Aug 2;1524:54-61. | | Reynosin protects against neuronal toxicity in dopamine-induced SH-SY5Y cells and 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats as models of Parkinson's disease: Reciprocal up-regulation of E6-AP and down-regulation of α-synuclein.[Pubmed: 23751361] | The aim of this study was to assess the effects of the sesquiterpene lactone Reynosin on dopamine (DA)-induced neuronal toxicity and regulation of E6-associated protein and α-synuclein proteins in both in vitro and in vivo models of Parkinson's disease.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Using flow cytometry and western blot analysis, we determined that Reynosin significantly protected both against cell death from dopamine-induced toxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells and against the loss of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive cells in 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-lesioned rats (a rodent Parkinson's disease model system). In addition, Reynosin made up-regulation of E6-associated protein expression and down-regulation of the over-expression of α-synuclein protein in both dopamine-treated SH-SY5Y cells and 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that the protective effect of Reynosin against dopamine-induced neuronal cell death may be due to the reciprocal up-regulation of E6-associated protein and down-regulation of α-synuclein protein expression. | | Pharm Biol. 2016 Nov;54(11):2623-2628. | | Reynosin and santamarine: two sesquiterpene lactones from Ambrosia confertiflora with bactericidal activity against clinical strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.[Pubmed: 27180996] |
Tuberculosis is primarily caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). Previous studies have shown that the dichloromethanic extract of Ambrosia confertiflora DC (Asteraceae) inhibited Mtb.
To isolate the compounds responsible for the mycobactericidal activity against clinical Mtb strains.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The dichloromethanic extract of aerial parts of A. confertiflora was separated using chromatography columns. Mycobactericidal activity of the isolated compounds was evaluated using the Alamar Blue bioassay (128-16 μg/mL, 7 days). Cytotoxicity was tested against normal cell line L929 using the MTT ([3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium]) assay (100-3.125 μg/mL, 48 h). Compound structures were elucidated by 1H and 13C uni- and bidimensional NMR.
Two sesquiterpene lactones (SQLs) with mycobactericidal activity were identified: santamarine and Reynosin. Reynosin was the most active compound, with a minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) of 128 μg/mL against the H37Rv, 366-2009 and 104-2010 Mtb strains and a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 64, 64, 128, 128 and 128 μg/mL against the H37Rv, 104-2010, 63-2009, 366-2009 and 430-2010 Mtb strains, respectively. Santamarine had MBCs of 128 μg/mL against the H3Rv and 104-2010 Mtb strains and MICs of 128 μg/mL against the H37Rv, 366-2009 and 104-2010 Mtb strains. We also isolated 1,10-epoxyparthenolide but only showed mycobacteriostatic activity (MIC 128 μg/mL) against the Mtb strain. Compounds were tested against the L929 cell line and the calculated selectivity index was <1.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first report of the mycobactericidal activity of these compounds against clinical Mtb strains. It is also the first report of the isolation of 1,10-epoxyparthenolide from A. confertiflora. The anti-mycobacterial activity of A. confertiflora was attributed to the SQLs identified. | | Planta Med. 2005 Aug;71(8):706-10. | | New sesquiterpene lactones from Laurus nobilis leaves as inhibitors of nitric oxide production.[Pubmed: 16142632] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two new metabolites 5alphaH,7alphaH-eudesman-4alpha,6alpha,11,12-tetraol (1) and 1beta,15-dihydroxy-5alphaH,7alphaH-eudesma-3,11(13)-dien-12,6alpha-olide ( 2) have been isolated from the methanolic extract of Laurus nobilis L. leaves. Their structures were determined through analysis of their one- and two-dimensional NMR spectral data ((1)H- and (13)C-NMR, DEPT, COSY, HMQC, HMBC and ROESY). The relative stereochemistry is proposed on the basis of combined J-based configuration analysis and ROESY data. In addition, three known sesquiterpene lactones santamarine (3), Reynosin (4) and costunolide (5) along with blumenol C (6) were isolated and identified by spectral means.
CONCLUSIONS:
The isolated compounds 1 - 6 were found to inhibit nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated murine macrophages. The most active compound 2 potently inhibited NO (2)(-) release with an IC (50) value of 0.8 microM. | | J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:365-74. | | Anti-inflammatory sesquiterpenes from Costus speciosus rhizomes.[Pubmed: 26593213 ] | Costus speciosus (Koen ex. Retz.) Sm. (crepe ginger, family Costaceae) is an ornamental plant used in traditional medicine for the treatment of inflammation, rheumatism, bronchitis, fever, headache, asthma, flatulence, constipation, helminthiasis, leprosy, skin diseases, hiccough, anemia, as well as burning sensation on urination.
The present study is designed to isolate and identify the active compounds from C. speciosus rhizomes and measure their anti-inflammatory activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The n-hexane-CHCl3 soluble fraction of the MeOH extract of C. speciosus rhizomes has been subjected to a repeated column chromatography, including normal silica gel and RP-18 column to give eight compounds. The structures of these compounds were established by UV, IR, 1D ((1)H and (13)C), and 2D ((1)H-(1)H COSY, NOESY, HSQC, and HMBC) NMR experiments and HRESIMS data. In addition, the anti-inflammatory activity of compounds 1-8 was evaluated by measuring the levels IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, COX-2, lipoxgenase-5, and PGE2 using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
The n-hexane-CHCl3 soluble fraction afforded a new eudesmane acid, specioic acid (8), along with seven known compounds, 22,23-dihydrospinasterone (1), dehydrodihydrocostus lactone (mokko lactone) (2), dehydrocostus lactone (3), stigmasterol (4), arbusculin A (5), santamarine (douglanin) (6), and Reynosin (7). Compounds 1, 4, and 5-7 were isolated for the first time C. speciosus. Compounds 1-4 displayed potent anti-inflammatory activity, while 7 and 8 showed moderate activity. Compounds 1-8 exhibited a concentration-related decrease in the levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, PGE2, lipoxgenase-5, and COX-2. Compounds 5 and 6 did not significantly decrease levels of different cytokines, PGE2, lipoxgenase-5, and COX-2 from PHA treatment at 1 μM. However, all tested compounds significantly decreased cytokines, PGE2, lipoxgenase-5, and COX-2 levels at concentration 100 μM. It is noteworthy that compounds 1-4 had the highest activity, where it lowered levels of cytokines, PGE2, lipoxgenase-5, and COX-2 to the extent that was no statistical difference from the control group. Thus, they decreased proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) with decreased level of the target enzymes (COX-2 and lipoxgenase-5) and subsequent reduction of its inflammatory product (PGE2).
CONCLUSIONS:
Good anti-inflammatory activities exhibited of the isolated compounds from C. speciosus corroborate the usefulness of this plant in the traditional treatment of inflammation and related symptoms. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)