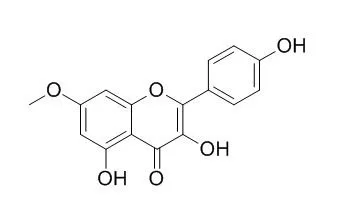
| Description: |
Rhamnocitrin can enhance the immune function, improve the formation of spleen cells of mice serum hemolysin of chicken red blood cell immune. Rhamnocitrin possesses significant anticataract activity and acts most likely due to its antioxidant property, it shows a significant protection against cloudiness in lenses induced by hydrogen peroxide and hydrocortisone in a dose dependent manner.Rhamnocitrin and kaempferol can augment cellular antioxidant defense capacity, at least in part, through regulation of HO-1 expression and MAPK signal transduction; they not only protect low-density lipoprotein from oxidation but also prevent atherogenesis through suppressing macrophage uptake of oxidized low-density lipoprotein. |
| Targets: |
HO-1 | ERK | MEK | p38MAPK | Immunology & Inflammation related |
| In vitro: |
| Oriental Pharmacy and Experimental Medicine,2012,12(3):227 -32. | | Anticataract activity of rhamnocitrin isolated from Bauhinia variegata stem bark.[Reference: WebLink] |
A cataract is any clouding or opaque area in the eye’s natural lens, which is normally crystal clear, is the leading cause of blindness worldwide. It accounts for approximately 42% of all blindness. Approximately 25% of the population over 65 and about 50% over 80 age has serious loss of vision because of cataract. Most cataracts progress and eventually hamper vision. Multiple mechanisms have been implicated in the development of cataract. But the exact pathogenesis which leads to opacification is not clearly known.
Oxidative damage to the lens has been recognized as the initiating event in the pathogenesis of cataracts.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In cataract, the oxidation-antioxidant equilibrium shift more towards oxidative stress. Accordingly, antioxidants could prove potential anticataract agents. Rhamnocitrin, a flavonoid, possess strong antioxidant effects; can be used effectively to manage the cataract. Therefore, anticataract activity of Rhamnocitrin (10, 20, 40 and 80 μg), isolated from Bauhinia variegata (Leguminosae) stem bark, was studied in ovine and chick embryo lens model. It showed a significant protection against cloudiness in lenses induced by hydrogen peroxide and hydrocortisone in a dose dependent manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
The findings suggest that Rhamnocitrin possess significant anticataract activity and act most likely due to its antioxidant property. |
|
| In vivo: |
| J Agric Food Chem. 2007 Nov 28;55(24):9969-76. | | Antiatherogenic effects of kaempferol and rhamnocitrin.[Pubmed: 17973448] | Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the arterial wall. Kaempferol and Rhamnocitrin (kaempferol 7-O-methyl ether) are two anti-inflammatory flavonoids commonly found in plants. The aim of this study is to investigate the function of kaempferol and Rhamnocitrin on prevention of atherosclerosis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Chemical analyses demonstrated that kaempferol and Rhamnocitrin were scavengers of DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl) with IC50 of 26.10 +/- 1.33 and 28.38 +/- 3.07 microM, respectively. Copper-induced low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation was inhibited by kaempferol and Rhamnocitrin, with similar potency, as measured by decreased formation of malondialdehyde and relative electrophoretic mobility (REM) on agarose gel, while Rhamnocitrin reduced delayed formation of conjugated dienes better than kaempferol. Cholesterol-laden macrophages are the hallmark of atherogenesis. The class B scavenger receptor, CD36, binds oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL), is found in atherosclerotic lesions, and is up-regulated by oxLDL. Addition of kaempferol and Rhamnocitrin (20 microM) caused significant reductions in cell surface CD36 protein expression in THP-1-derived macrophages (p < 0.05). Reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-Q-PCR) showed that kaempferol and Rhamnocitrin (20 microM) decreased oxLDL-induced CD36 mRNA expression (p < 0.01 and p < 0.05, respectively). Kaempferol- and Rhamnocitrin-treated macrophages also showed reduction in 1,1'-dioctadecyl-3,3,3',3'-tetramethylindocarbocyanide perchlorate (DiI)-labeled oxLDL uptake.
CONCLUSIONS:
Current evidences indicate that kaempferol and Rhamnocitrin not only protect LDL from oxidation but also prevent atherogenesis through suppressing macrophage uptake of oxLDL. | | J Chromatogr Sci . 2016 Oct 17;54(9):1605-1612. | | Simultaneous Determination of Formononetin, Calycosin and Rhamnocitrin from Astragalus Complanatus by UHPLC-MS-MS in Rat Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study[Pubmed: 27325683] | | Abstract
This assay provided a novel and generally applicable method to simultaneously determine formononetin, calycosin and Rhamnocitrin in rat plasma based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. A single step of protein precipitation procedure with methanol was utilized, and luteolin was chosen as an internal standard. Chromatographic separation was achieved using a Waters Symmetry-C18 column, and the applied isocratic elution program allowed for the simultaneous determination of the three flavones in a one-step chromatographic separation with a total run time of 3.5 min. The fully validated methodology for the analytes demonstrated high sensitivity, good accuracy and precision. The average recoveries of the analytes and internal standard were all above 91.0% and no obvious matrix effect was observed. This method was successfully applied to the preclinical pharmacokinetic studies of formononetin, calycosin and Rhamnocitrin in rats. The results would be helpful to provide some references to clinical application of this herb. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)