| Structure Identification: |
| Journal of the Korean Wood Science and Technology,2000,28(3):52-61. | | Extractives of the Wood of Black Locust and the Bark of Poplar as Decay-Resistant Hardwood Tree Species.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Black locust(Robinia pseudoacacia) and poplar(Populus alba glandulosa) trees were collected, extracted with acetone-(7:3, v/v) after drying, fractionated with hexane, chloroform and ethylacetate, and freeze dried to get some brown powder. Each fraction of the powder was chromatographed on a Sephadex LH-20 column using a series of aqueous methanol and ethanol-hexane mixture as eluting solvents.
CONCLUSIONS:
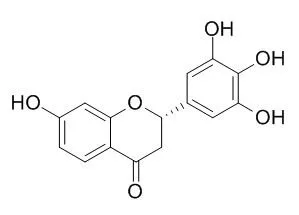
The wood extractives of black locust contained (+)-leucorobinetinidin as flavan, Robtin as flavanone and dihydrorobinetin as flavanonol, and robinetin as flavonol. The poplar bark extractives contained various kinds of phenolic compounds : (+)-catechin as flavan, naringeoin, eriodictyol, sakuranetin, aromadendrin and taxifolin as flavanonol, salireposide as salicin derivative, and minor compounds such as aesculin and p-coumaric acid. However, aesculin has not been reported as a constituent of the poplar bark in Korea yet. NMR and FAB-MS analyses were done to elucidate the structures of isolated phenolic constituents. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)