| In vitro: |
| Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 May 15;308(10):L1068-77. | | Roflumilast combined with adenosine increases mucosal hydration in human airway epithelial cultures after cigarette smoke exposure.[Pubmed: 25795727] | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a growing cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Recent studies have shown that cigarette smoke (CS) induces cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) dysfunction, which leads to airway-surface liquid (ASL) dehydration. This in turn contributes to the mucus dehydration and impaired mucociliary clearance that are seen in the chronic bronchitis form of COPD. Roflumilast is a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor that may improve lung function and reduce the frequency of exacerbations in patients with COPD. Although Roflumilast can affect cAMP metabolism, little is known about the downstream pharmacological effects in the airways.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We hypothesized that Roflumilast would increase ASL rehydration in human bronchial epithelial cultures (HBECs) after chronic CS exposure. cAMP production was measured by Förster resonance energy transfer in HEK293T cells and by ELISA in HBECs. ASL height was measured by xz-confocal microscopy after air exposure or following HBEC exposure to freshly produced CS. Roflumilast had little effect on cAMP or ASL height when applied on its own; however, Roflumilast significantly potentiated adenosine-induced increases in cAMP and ASL height in CS-exposed HBECs. Roflumilast increased the rate of ASL height recovery in cultures after CS exposure compared with controls. In contrast, the β2-adrenergic receptor agonists isoproterenol and salmeterol failed to increase ASL height after CS exposure.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our data suggest that Roflumilast can increase ASL hydration in CS-exposed HBECs, which is predicted to be beneficial for the treatment of mucus dehydration/mucus stasis in patients with COPD chronic bronchitis. | | J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Apr;297(1):267-79. | | Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory potential of the novel PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in vitro.[Pubmed: 11259554] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
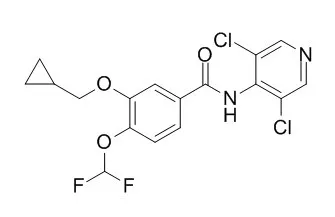
From a series of benzamide derivatives, Roflumilast (3-cyclo-propylmethoxy-4-difluoromethoxy-N-[3,5-di-chloropyrid-4-yl]-benzamide) was identified as a potent and selective PDE4 inhibitor. It inhibits PDE4 activity from human neutrophils with an IC(50) of 0.8 nM without affecting PDE1 (bovine brain), PDE2 (rat heart), and PDE3 and PDE5 (human platelets) even at 10,000-fold higher concentrations. Roflumilast is almost equipotent to its major metabolite formed in vivo (Roflumilast N-oxide) and piclamilast (RP 73401), however, more than 100-fold more potent than rolipram and Ariflo (cilomilast; SB 207499). The anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory potential of Roflumilast and the reference compounds was investigated in various human leukocytes using cell-specific responses: neutrophils [N-formyl-methyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP)-induced formation of LTB(4) and reactive oxygen species (ROS)], eosinophils (fMLP- and C5a-induced ROS formation), monocytes, monocyte-derived macrophages, and dendritic cells (lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha synthesis), and CD4+ T cells (anti-CD3/anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody-stimulated proliferation, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, and interferon-gamma release). Independent of the cell type and the response investigated, the corresponding IC values (for half-maximum inhibition) of Roflumilast were within a narrow range (2-21 nM), very similar to Roflumilast N-oxide (3-40 nM) and piclamilast (2-13 nM). In contrast, cilomilast (40-3000 nM) and rolipram (10-600 nM) showed greater differences with the highest potency for neutrophils. Compared with neutrophils and eosinophils, representing the terminal inflammatory effector cells, the relative potency of Roflumilast and its N-oxide for monocytes, CD4+ T cells, and dendritic cells is substantially higher compared with cilomilast and rolipram, probably reflecting an improved immunomodulatory potential.
CONCLUSIONS:
The efficacy of Roflumilast in vitro and in vivo (see accompanying article in this issue) suggests that Roflumilast will be useful in the treatment of chronic inflammatory disorders such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Toxicol Pathol. 2015 Jun;43(4):569-80. | | Roflumilast-induced Local Vascular Injury Is Associated with a Coordinated Proteome and Microparticle Change in the Systemic Circulation in Pigs.[Pubmed: 25311372] | Drug-induced vascular injury (DIVI) is commonly associated with phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors. Despite histological characterization, qualified biomarkers for DIVI detection are lacking.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated whether a single administration of Roflumilast (PDE-IV inhibitor) induces vascular damage and identified novel surrogate biomarkers of acute vascular injury. Pigs received postoperative 250, 375, or 500 μg of Roflumilast or placebo/control. After 1.5 hr, coronary reactivity was determined by catheter-based administration of acetylcholine and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) in the coronary sinus. Immunohistochemical analysis of vessel integrity (von Willebrand factor [vWF]) and fibrin(ogen) deposition was performed in the coronary artery and aorta. Peripheral blood was collected for differential proteomics and microparticles analysis. Circulating interleukin (IL)-6 was analyzed. Roflumilast-treated animals displayed higher vasodilation to acetylcholine and SNP versus controls (p < .05). Roflumilast-treated animals showed a dose-dependent (p < .05) decrease in vessel integrity and dose-dependent increase in fibrin deposition forming a continuous layer at Roflumilast-500 μg. Peripheral blood of Roflumilast-500-μg-treated animals showed increased levels of total and endothelial-derived microparticles and exhibited a coordinated change in proteins kininogen-1, endothelin-1, gelsolin, apolipoprotein A-I, and apolipoprotein-J associated with vascular injury (p < .05 vs. controls). IL-6 remained unaltered.
CONCLUSIONS:
Roflumilast-induced vascular injury can be detected by novel markers in peripheral blood. Validation of these surrogate markers in human samples seems required. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)