| In vitro: |
| Molecules. 2014 Dec 4;19(12):20340-9. | | Saikosaponin D isolated from Bupleurum falcatum inhibits selectin-mediated cell adhesion.[Pubmed: 25486247] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three saikosaponins were isolated from the MeOH extract of the roots of Bupleurum falcatum L.: saikosaponin B3 (1); Saikosaponin B4 (2); and saikosaponin D (3). Of the three, compound 3 inhibited the interaction of selectins (E, L, and P) and THP-1 cells with IC50 values of 1.8, 3.0 and 4.3 μM, respectively. Also, the aglycone structure 4 of compound 3 showed moderate inhibitory activity on L-selectin-mediated cell adhesion.
CONCLUSIONS:
From these results, we suspect that compound 3 isolated from Bupleurum falcatum roots would be a good candidate for therapeutic strategies to treat inflammation. | | Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1980, 28(6):1788-1794. | | Effects of saikosaponins on the metabolic actions of adrenaline, ACTH and insulin on the fat cells.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Saikosaponins a and d inhibited adrenaline-induced lipolysis in fat cells isolated from epididymal adipose tissue of rats. Saikosaponin a, Saikosaponin b1, Saikosaponin b2, Saikosaponin B4, Saikosaponin c and Saikosaponin d inhibited ACTH-induced lipolysis in the fat cells. Insulin-stimulated lipogenesis in adipose tissue was significantly reduced by saikosaponin d.
CONCLUSIONS:
Propranolol (a β-blocker) inhibited not only lipolytic actions induced by adrenaline and ACTH but also lipogenesis stimulated by insulin. In contrast to propranolol, saikosaponins b1, b2, b4 and c selectively inhibited ACTH-induced lipolysis without affecting the lipogenetic effect of insulin. The structure-activity relationship of saikosaponins is discussed. |
|


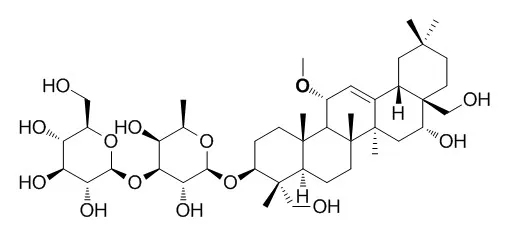



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)