| In vivo: |
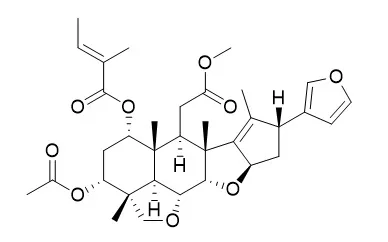
| J Chem Ecol. 1996 Aug;22(8):1453-61. | | Insect antifeedant and growth-regulating activities of Salannin and other c-seco limonoids from neem oil in relation to Azadirachtin.[Pubmed: 24226248] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antifeedant and insect growth-regulating activities of Salannin, nimbin, and 6-deacetylnimbin, in comparison with azadirachtin-A, have been studied againstSpodoptera litura, Pericallia ricini, andOxya fuscovittata. Salannin deterred feeding, delayed molt by increasing larval duration, caused larval and pupal mortalities, and decreased pupal weights in the two lepidopterans. Salannin also caused molt delays and nymphal mortalities inOxya fuscovittata.
CONCLUSIONS:
The role of Salannin and other compounds in conferring bioactivity, along with azadirachtin-A, to neem oil/neem seed extracts is emphasized. | | J Oleo Sci. 2011;60(2):53-9. | | The melanogenesis-inhibitory, anti-inflammatory, and chemopreventive effects of limonoids in n-hexane extract of Azadirachta indica A. Juss. (neem) seeds.[Pubmed: 21263200] | Seventeen limonoids (tetranortriterpenoids 1-17) were isolated from the n-hexane extract of Azadirachta indica (neem) seeds.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The previously unidentified compound 16 was established by spectroscopy to be 17-defurano-17-oxoSalannin. The effects of six compounds, 6 and 11-15, on melanogenesis in B16 melanoma cells was evaluated; 2 compounds, Salannin (13) and 3-deacetylSalannin (15), exhibited marked inhibitory effects (70-74% reduction of melanin content at 25 μg/mL) with only minor cytotoxicity (79-85% of cell viability). Eleven compounds, 2, 3, 5, 6, and 9-15, were evaluated for inhibitory activity against 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced inflammation (1.7 nmol/ear) in mice; all exhibited marked anti-inflammatory activity (ID(50) values 0.22-0.57 μmol/ear). In addition, compounds 6 and 11-16 exerted moderate inhibition (IC(50) values of 410-471 mol ratio/32 pmol TPA) of TPA-induced Epstein-Barr virus early antigen (EBV-EA) activation in Raji cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
The triacylglycerol fraction of the n-hexane extract contained oleic acid (50.2%) as the most predominant fatty acid constituent. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)