| In vitro: |
| Planta Med. 2011 Jul;77(11):1183-8. | | Antiproliferative constituents of the roots of Conyza canadensis.[Pubmed: 21294076] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
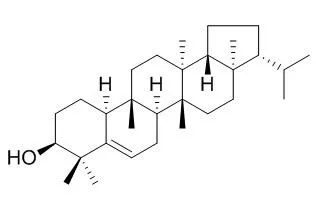
Bioassay-guided fractionation of the N-hexane and CHCl₃ phases of the methanol extract of the roots of Conyza canadensis (L.) Cronquist led to the isolation of two new dihydropyranones named conyzapyranone A (1) and B (2), and the known 4 Z,8 Z-matricaria- γ-lactone (3), 4 E,8 Z-matricaria- γ-lactone (4), 9,12,13-trihydroxy-10(E)-octadecenoic acid (5), epifriedelanol (6), friedeline (7), taraxerol (8), Simiarenol (9), spinasterol (10), stigmasterol, β-sitosterol, and apigenin. The structures were determined by means of ESIMS and 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy, including ¹H-¹H COSY, NOESY, HSQC, and HMBC experiments. The isolated compounds were evaluated for their antiproliferative activities and were demonstrated to exert considerable cell growth-inhibitory activity against human cervix adenocarcinoma (HeLa), skin carcinoma (A431), and breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7) cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Some of the active components, including 2, 4, and 10, proved to be substantially more potent against these cell lines than against noncancerous human foetal fibroblasts (MRC-5) and can therefore be considered selective antiproliferative natural products. | | Saudi Pharm J. 2017 Feb;25(2):236-40. | | Biologically-guided isolation of leishmanicidal secondary metabolites from Euphorbia peplus L.[Pubmed: 28344474 ] |
Leishmaniasis is a worldwide health problem, highly endemic in developing countries. Moreover, the severe side effects and the reported drug resistance make it an urgent need to search for effective drugs that can replace or supplement those currently used.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In a research program designed to investigate the antileishmanial activity of plants collected from the Egyptian flora, twenty extracts from fifteen plants growing in Egypt have been investigated for in vitro leishmanicidal activity against Leishmania donovani promastigotes. Among the tested extracts, the methanol extract of Euphorbia peplus aerial parts exhibited a significant antileishmanial activity as it produced 100% inhibition of growth with activity similar to amphotericin B. The total extract was subjected to liquid-liquid fractionation using solvents of different polarities, followed by testing the antileishmanial activity of the successive fractions. Phytochemical exploration of the active n-hexane fraction (which produced 75% inhibition of growth) led to isolation of four compounds: Simiarenol (1), 1-hexacosanol (2), β-sitosterol (3), and β-sitosterol-3-O-glucoside (4) from the biologically active sub-fractions. Structure elucidation was aided by 1D and 2D NMR techniques.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, E. peplus plant has many non-polar secondary metabolites that can be used as drug leads for treatment of leishmaniasis. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)