| Kinase Assay: |
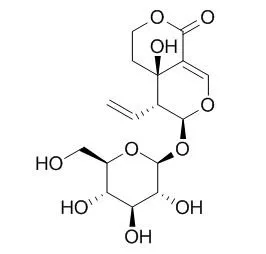
| Physiol Behav. 2015 May 15;144:66-72. | | Role of 5-HT2 receptors in diabetes: Swertiamarin seco-iridoid glycoside might be a possible 5-HT2 receptor modulator.[Pubmed: 25708274] | In the present review, we are focusing on modulators of 5-HT2 receptors, Swertiamarin and their role in diabetes. These drugs possess both central and peripheral actions in various animal models of depression, diabetes and obesity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Swertiamarin and 5-HT2 antagonist are reported antidepressant, hypolipidemic and beneficial in peripheral vasculopathy. In contrast to this, 5-HT2C selective agonist decreases hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia and insulin secretogogue by action. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are known antidepressant having weight gain as an adverse effect. Swertiamarin has similar pharmacological actions as 5-HT2 antagonist and 5-HT2C selective agonist. This warrants that Swertiamarin might modulate 5-HT2 receptors rather than affecting the uptake of serotonin.
CONCLUSIONS:
In the light of present investigation, the mechanism of these drugs can correlate the role of central and peripheral 5-HT2 receptors in diabetes. | | Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014 Jun 2;56:70-86. | | Swertiamarin attenuates inflammation mediators via modulating NF-κB/I κB and JAK2/STAT3 transcription factors in adjuvant induced arthritis.[Pubmed: 24582615] | Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune and chronic inflammatory disease that leads to pannus formation followed by severe joint destruction, characterized by synovial hyperplasia, inflammation and angiogenesis. Swertiamarin is a secoiridoid glycoside that is used as an anti-inflammatory compound, mainly found in Enicostema axillare (Lam) A. Raynal, a medicinal plant used in Indian system of traditional medicine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, the effect of Swertiamarin was evlauated in experimental adjuvant arthritis animal model by the estimation of biochemical (paw thickness, lysosomal enzymes, and urinary degradative products) parameters, proinflammatory cytokines and enzymes along with histopathological and radiographic observations. The proteins of phosphorylated NF-κB/IκB and JAK2/STAT3 transcription factors were also quantified from experimental animals as well as LPS induced RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. In in silico analysis, Swertiamarin was docked with proinflammatory enzymes to confirm its potential. The administration of Swertiamarin (2, 5, 10mg/kg bw) significantly (P⩽0.05) inhibited the levels of paw thickness, lysosomal enzymes and increased the body weight of experimental animals in a dose dependent manner. In molecular analysis, the treatment decreased the release of proinflammatory cytokines (IL1, TNF, IL-6) and proangiogenic enzymes (MMPs, iNOS, PGE2, PPARγ and COX-2); and also significantly (P⩽0.05) increased the levels of antiinflammatory proteins (IL-10, IL-4) when compared to the disease groups. The Swertiamarin treatment significantly (P⩽0.05) inhibited the release of NF-κB p65, p-IκBα, p-JAK2 and p-STAT3 signaling proteins levels on both experimental animals and LPS induced cells. Histopathological and radiological analysis evidenced the curative effect of Swertiamarin on bone destruction. The docking studies of Swertiamarin on proinflammatory enzymes supported the results from the in vivo experiments.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus the Swertiamarin inhibited the development of arthritis by modulating NF-κB/IκB and JAK2/STAT3 signaling. These findings suggested that Swertiamarin acted as an anti-rheumatic agent. |
|
| Animal Research: |
| J Endocrinol Invest. 2015 Jun;38(6):669-84. | | Immunohistochemistry, histopathology, and biomarker studies of swertiamarin, a secoiridoid glycoside, prevents and protects streptozotocin-induced β-cell damage in Wistar rat pancreas.[Pubmed: 25770453] | Diabetes mellitus is globally the major cause for metabolic syndrome in STZ-induced diabetic rats, leading to mortality. Treatment of diabetes by oral hypoglycemic agents causes adverse side effects and thus treatment with natural herbal drugs like Swertiamarin is promising. Swertiamarin, an active compound isolated from Enicostemma littorale possesses antidiabetic activity and enhances β cell regeneration which causes reversal of diabetes. The present study aims at the following: (1) to evaluate antidiabetic, anti-hyperlipidaemic, activity of Swertiamarin in Streptozotocin- induced diabetic rats using biomarkers. (2) To assess histopathological alterations in Pancreas, Liver, Kidney, and Heart of Swertiamarin-treated STZ-induced diabetic rats and confirm cytoprotective activity of Swertiamarin by Immunohistochemistry and morphometric investigations.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Diabetes was induced intraperitoneally in male Wistar rats by Streptozotocin (STZ 50 mg/kg). After STZ-induction, hyperglycemic rats were treated with doses of Swertiamarin orally (15, 25, 50 mg/kg) each for 28 days. Glibenclamide (2.5 mg/kg), a sulphonyl urea, was used as a standard drug. The glycemic control was measured by the biochemical parameter assays. Histopathology analysis of organs and immunohistochemistry of islets were carried out. Our study results showed that oral administration of Swertiamarin at a dosage of 15, 25, 50 mg/kg bw for 28 days resulted in a significant (p < 0.01) decrease in fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, TC, TG, LDL, and increased the levels of hemoglobin, plasma insulin, TP, body weight, and HDL levels significantly (p < 0.01) when compared to STZ-induced diabetic rats, as confirmed by immunohistochemical studies. The effect of Swertiamarin on Carbohydrate-metabolizing enzymes was investigated and found to have normal therapeutic activity. Histopathological studies of Pancreas of Swertiamarin-treated diabetic rats showed regeneration of islets when compared to STZ-induced diabetic rats, as confirmed by immunohistochemical studies.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our research results clearly substantiate that Swertiamarin possesses antihyperglycemic, antihyperlipidemic, cytoprotective, and immune reactivity and also a broad spectrum potential of treating diabetes and other complications related to diabetes and hence can be developed into a potent oral antidiabetic drug. | | Phytomedicine. 2009 Mar;16(2-3):227-32. | | Antinociceptive activity of swertiamarin isolated from Enicostemma axillare.[Pubmed: 19019644 ] | Many traditional Indian medicinal plants which contain large quantity of a secoiridoid, Swertiamarin are being used to relieve pain. Iridoids present in a wide variety of medicinal plants possess a large number of medicinal properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study in vivo antinociceptive activity of Swertiamarin isolated from E. axillare was carried out using three different methods in mice. In the hot plate method, a significant increase in the latency period was observed for the treatment with Swertiamarin at 100 and 200 mg/kg bw after 30 and 45 min. The percent protection observed after 45 min was 109.42, 147.42 and 157.14, respectively, for the standard paracetamol and Swertiamarin at 100 and 200 mg/kg bw treatments. A significant increase in the tail withdrawal reflex was observed for the Swertiamarin treatment at both the doses with percent protections of 150 and 200, respectively. In both these methods, Swertiamarin produced potent activity than that of standard paracetamol. In the acetic acid induced writhing, Swertiamarin at 100 and 200 mg/kg bw reduced the number of writhes significantly. Dose dependent results were observed in all the three methods and among the two doses, Swertiamarin at 200 mg/kg bw showed potent activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results prove that Swertiamarin possess both peripheral and central antinociceptive activity. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)