| In vitro: |
| PLoS One. 2015 Nov 23;10(11):e0143530. | | Extracts from Field Margin Weeds Provide Economically Viable and Environmentally Benign Pest Control Compared to Synthetic Pesticides.[Pubmed: 26599609 ] | Plants with pesticidal properties have been investigated for decades as alternatives to synthetics, but most progress has been shown in the laboratory. Consequently, research on pesticidal plants is failing to address gaps in our knowledge that constrain their uptake. Some of these gaps are their evaluation of their efficacy under field conditions, their economic viability and impact on beneficial organisms.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Extracts made from four abundant weed species found in northern Tanzania, Tithonia diversifolia, Tephrosia vogelii, Vernonia amygdalina and Lippia javanica offered effective control of key pest species on common bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris) that was comparable to the pyrethroid synthetic, Karate. The plant pesticide treatments had significantly lower effects on natural enemies (lady beetles and spiders). Plant pesticide treatments were more cost effective to use than the synthetic pesticide where the marginal rate of return for the synthetic was no different from the untreated control, around 4USD/ha, compared to a rate of return of around 5.50USD/ha for plant pesticide treatments.
Chemical analysis confirmed the presence of known insecticidal compounds in water extracts of T. vogelii (the rotenoid deguelin) and T. diversifolia (the sesquiterpene lactone Tagitinin A). Sesquiterpene lactones and the saponin vernonioside C were also identified in organic extracts of V. amygdalina but only the saponin was recorded in water extracts which are similar to those used in the field trial.
CONCLUSIONS:
Pesticidal plants were better able to facilitate ecosystem services whilst effectively managing pests. The labour costs of collecting and processing abundant plants near farm land were less than the cost of purchasing synthetic pesticides. | | J Nat Prod. 2015 May 22;78(5):1083-92. | | Phytotoxins from Tithonia diversifolia.[Pubmed: 25879678 ] | Tithonia diversifolia (Mexican sunflower) is a dominant plant of the Asteraceae family, which suggests it produces allelochemicals that interfere with the development of surrounding plants. The study described herein was conducted to identify the compounds that have phytotoxic activity in T. diversifolia extracts.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
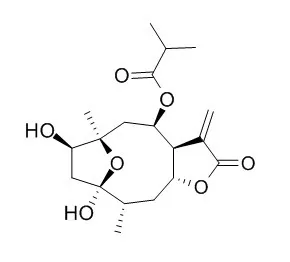
Ethyl acetate extracts of the leaves, stems, and roots showed significant inhibition of wheat coleoptile growth, and the leaf extract had similar inhibitory effects to a commercial herbicide. Fourteen compounds, 12 of which were sesquiterpene lactones, have been isolated. Two sesquiterpene lactones are reported for the first time and were isolated as an inseparable mixture of 8β-O-(2-methylbutyroyl)tirotundin (4) and 8β-O-(isovaleroyl)tirotundin (5). Their structures were determined by spectroscopic analysis, including NMR techniques and mass spectrometry. The sesquiterpene lactones 1β-methoxydiversifolin (6), Tagitinin A (7), and tagitinin C (8) were the major products identified.
CONCLUSIONS:
These compounds were active on etiolated wheat coleoptiles, seed germination, and the growth of STS and weeds. The phytotoxic activity shown by these sesquiterpene lactones indicates that they are the compounds responsible for the activity exhibited by the initial extracts. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)