| Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2007 Aug;71(8):2065-8. |
| Tryptophol induces death receptor (DR) 5-mediated apoptosis in U937 cells.[Pubmed: 17690453] |
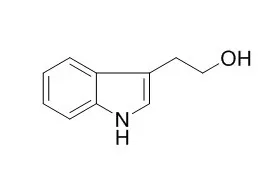
Tryptophol is a natural component isolated from vinegar produced from the boiled extract of black soybean. We have reported that Tryptophol induces apoptosis in U937 cells via activation of caspase-8 followed by caspase-3. Tryptophol, however, did not affect human peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we found that Tryptophol enhances formation of a death-inducing signaling complex including death receptor (DR) 5. Cell viability and induction of apoptosis by Tryptophol was reduced by transfection with decoy receptor (DcR) 1.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Tryptophol induces apoptosis through DR5 and that the resistance of PBL to Tryptophol-induced apoptosis might be due to competition from DcR1. |
| Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008 May;102(5):443-52. |
| Genotoxicity of tryptophol in a battery of short-term assays on human white blood cells in vitro.[Pubmed: 18248512] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The genotoxic effects of Tryptophol (indole-3-ethanol), an aromatic alcohol and known secondary metabolite of the opportunistic yeast Candida albicans and other Candida spp. The results obtained suggest cytotoxic, cytostatic and genotoxic effects of the Tryptophol treatment in vitro that were mainly dose-dependent. The type and the extent of DNA lesions detected in Tryptophol-treated samples indicate the possibility that observed damage is mediated by highly reactive aldehyde metabolite and/or free radicals produced by treatment. The results show that mortality of lymphocytes in Tryptophol-treated samples was primarily caused by apoptosis. The generation of additional DNA strand breaks and cytogenetic consequences (chromosome aberrations, sister chromatid exchanges and micronuclei), as observed in this study, sustain the possibility that Tryptophol toxicity is mediated by the formation of DNA cross-links and aldehyde-protein adducts.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, this preliminary study elucidates only a part of Tryptophol toxicity to human cells. Because current evidence is not sufficient to obtain information relevant for human risk assessment, further in vitro and in vivo studies are essential in order to clarify remaining issues, especially to elucidate the exact mechanisms and nature of the damage produced following treatment as well to estimate possible interindividual variability in genotoxic responses to the chemical. |
| Experientia. 1976 May 15;32(5):645-7. |
| The effects of tryptophol on immune responses and it implications toward trypanosome-induced immunosuppression.[Pubmed: 776647] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Daily administration of Tryptophol to laboratory rodents resulted in significantly depressed antibody production of heterologous red blood cell challenge, did not alter cellular-mediated responses to oxazalone.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that trypanosome-produced Tryptophol may account for the immunodepression observed during trypanosomiasis. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)