| In vitro: |
| Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(51):12692-12699. | | New triterpenoids and other constituents from the fruits of Benincasa hispida (Thunb.) Cogn.[Pubmed: 24313299 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
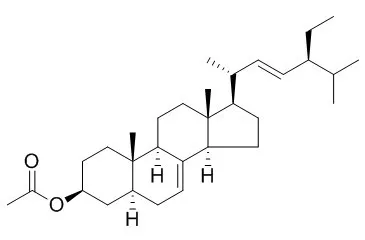
Benincasa hispida (Thunb.) Cogn. fruits are widely consumed in China and tropical countries. This study identifies three new triterpenoids, 3α,29-O-di-trans-cinnamoyl-D:C-friedooleana-7,9(11)-diene (1), oleanolic acid 28-O-β-d-xylopyranosyl-[β-d-xylopyranosyl-(1→4)]-(1→3)-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-l-arabinopyranoside (2), and oleanolic acid 28-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-β-d-xylopyranosyl-[β-d-xylopyranosyl-(1→4)]-(1→3)-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-l-arabinopyranoside (3), together with 12 known compounds, multiflorenol (4), isomultiflorenyl acetate (5), stigmasterol (6), stigmasterol 3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (7), α-spinasterol (alpha-Spinasterol acetate,8), α-spinasterol 3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (9), β-sitosterol (10), daucosterol (11), arbutin (12), nicotinic acid (13), (+)-pinonesinol (14), and ethyl β-d-glucopyranoside (15). The structures of compounds 1-15 were determined by spectroscopic and chemical methods.
CONCLUSIONS:
All the compounds with the exception of 4, 5, and 9-11 were isolated from B. hispida for the first time. The anticomplement activities of compounds 1-15 were assessed by Mayer's modified method. Compounds 1-15 showed no significant cytotoxic activity against HeLa human cervical, HL-60 human hepatoma, and SMMC-7721 human hepatoma cell lines. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Planta Medica, 2004, 70(08):736-739. | | alpha-Spinasterol isolated from the root of Phytolacca americana and its pharmacological property on diabetic nephropathy.[Pubmed: 15326549 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Based on an inhibitory activity-guided fractionation for the high glucose-induced proliferation of glomerular mesangial cells (GMCs), chloroform extracts of the roots of Phytolacca americana were found to contain alpha-spinasterol(alpha-Spinasterol acetate) (C (29)H (48)O), a delta (7)-sterol. This phytosterol proved to be a potent inhibitor (IC (50) = 3.9 x 10 (-12) g/mL, 9.5 pmol/L) of glomerular mesangial cell proliferation caused by high-ambient glucose (5.6 mM vs. 25 mM), and its inhibitory potency was about 1,000 times higher than that of simvastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor used as a positive control. alpha-Spinasterol also significantly reduced the increases of serum triglycerides, renal weight and urinary protein excretion in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice, and these were comparable to the results observed in insulin-treated diabetic mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, the results obtained in this study suggest that alpha-spinasterol has a significant therapeutic potential to modulate the development and/or progression of diabetic nephropathy. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)