| In vitro: |
| Planta Med. 2008 Jun;74(8):867-9. | | Inhibitory constituents of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in BV2 microglia isolated from Amomum tsao-ko.[Pubmed: 18523923] | A methanolic extract of the fruits of AMOMUM TSAO-KO (Zingiberaceae) significantly attenuated nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-simulated BV2 microglia.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
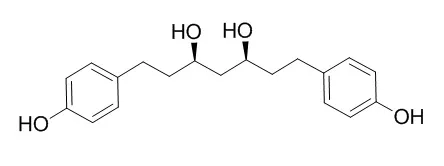
Two new bicyclic nonanes characterized as 6,7-dihydroxy-indan-4-carbaldehyde ( 1) and 6-hydroxy-indan-4-carbaldehyde ( 2) were isolated with the eleven known compounds 6,7-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethyloct-2-enoic acid ( 3), tsaokoin ( 4), isotsaokoin ( 5), 8-oxogeraniol ( 6), P-menth-1-ene-5,6-diol ( 7), 3alpha-hydroxycarvotagenone ( 8), tsaokoarylone ( 9), 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-4,6-heptadien-3one ( 10), (+)-hannokinol ( 11), meso-Hannokinol ( 12) and hannokinin ( 13), from the fruits of A. TSAO-KO using bioactivity-guided fractionation.
CONCLUSIONS:
All thirteen compounds significantly inhibited lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in BV2 microglial cells at concentrations ranging from 1 microM to 100 microM. | | Food Funct. 2014 Aug;5(8):1747-54. | | Bioactivity evaluation of ingredients identified from the fruits of Amomum tsaoko Crevost et Lemaire, a Chinese spice.[Pubmed: 24915829] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work, a phytochemical investigation was conducted on Amomum tsaoko Crevost et Lemaire, a traditional Chinese spice. Based on spectroscopic methods including MS, (1)H-NMR, (13)C-NMR, DEPT135 and HMQC spectroscopy, eight main chemical compositions, sitosterol, daucosterol, meso-Hannokinol, quercetin, epicatechin, quercetin-7-O-β-glucoside, quercetin-3-O-β-glucoside, and catechol, were isolated and identified from A. tsaoko, among which quercetin, quercetin-7-O-β-glucoside and quercetin-3-O-β-glucoside were first found in A. tsaoko.
CONCLUSIONS:
Their bioactivities were evaluated by the inhibitory effect on NO production in LPS-stimulated macrophage RAW 264.7 cells, the protective effect on H2O2-induced apoptosis of PC-12 cells and the DPPH radical scavenging assay. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)