Natural Products

- ChemFaces is a professional high-purity natural products manufacturer.
- Product Intended Use
- 1. Reference standards
- 2. Pharmacological research
- 3. Inhibitors



| Size /Price /Stock | 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO / $193.0 / In-stock | Other Packaging | *Packaging according to customer requirements(100uL/well, 200uL/well and more), and Container use Storage Tube With Screw Cap |

| Size /Price /Stock | 10 mM * 100 uL in DMSO / Inquiry / In-stock 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO / Inquiry / In-stock | Related Libraries |
| Description: | Reference standards. |
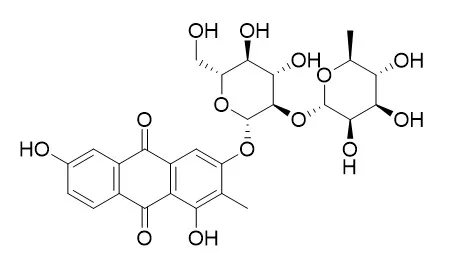
| Source: | The herbs of Pittosporum illicioides |
| Solvent: | DMSO, Pyridine, Methanol, Ethanol, etc. |
| Storage: | Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to 24 months(2-8C). Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour. Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com |
| After receiving: | The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling. |
 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7286 mL | 8.643 mL | 17.2861 mL | 34.5722 mL | 43.2152 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3457 mL | 1.7286 mL | 3.4572 mL | 6.9144 mL | 8.643 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1729 mL | 0.8643 mL | 1.7286 mL | 3.4572 mL | 4.3215 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0346 mL | 0.1729 mL | 0.3457 mL | 0.6914 mL | 0.8643 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0173 mL | 0.0864 mL | 0.1729 mL | 0.3457 mL | 0.4322 mL |
| Structure Identification: |
|