METHODS AND RESULTS:
By bioactivity-directed fractionation, six cytotoxic constituents have been characterized from the bark of Plumeria rubra collected in Indonesia.
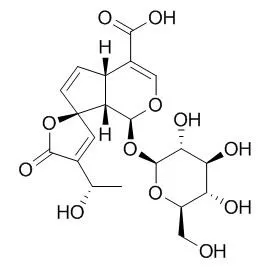
Three iridoids, fulvoplumierin [1], allamcin [2], and allamandin [3], as well as 2,5-dimethoxy-p-benzoquinone [4], were found to be active constituents of the P. rubra petroleum-ether- and CHCl3-soluble extracts. Cytotoxic compounds isolated from the H2O-soluble extract of the bark were the iridoid plumericin [5], and the lignan liriodendrin [6]. Each of these substances was found to demonstrate general cytotoxic activity when evaluated with a panel of cell lines composed of murine lymphocytic leukemia (P-388) and a number of human cancer cell-types (breast, colon, fibrosarcoma, lung, melanoma, KB). Five additional iridoids, 15-Demethylplumieride [7], plumieride [8], alpha-allamcidin [9], beta-allamcidin [10], and 13-O-trans-p-coumaroylplumieride [11], were obtained as inactive constituents.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compound 7 was found to be a novel natural product, and its structure was determined by spectroscopic methods and by conversion to plumieride [8].
The configuration of the C-4 stereocenter was unambiguously assigned for compounds 9 and 10, and certain nmr reassignments have been provided for compound 1. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)