| In vitro: |
| Natural product communications, 2013, 8(9):1255-1256. | | Cytotoxic activity of dihydrochalcones isolated from Corema album leaves against HT-29 colon cancer cells.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
During our search for cytotoxic compounds from Andalusian vascular plants, the ethyl acetate extract from the leaves of Corema album (L.) D. Don (Ericaceae) was selected for its cytotoxic activity against the HT-29 human colon adenocarcinoma cell line. Two dihydrochalcones,
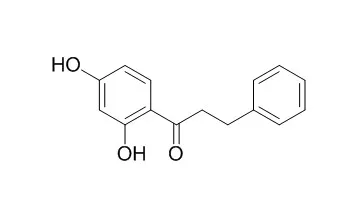
2',4'-Dihydroxydihydrochalcone (1) and 2'-methoxy-4'-hydroxydihydrochalcone (2), have been isolated from the leaves of C. album. Their structural identification was based on 1H NMR and 13C NMR data, including 2D NMR, and mass spectrometry. These compounds were subjected to the sulfhorhodamine B (SRB) cytotoxic assay against human colon adenocarcinoma cells (HT-29).
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1 and 2 showed higher cytotoxicity than the positive control 5-fluorouracil (5-FU); the IC50 values (microM +/- SEM) were 1.8 +/- 0.4 for compound 1, 8.5 +/- 2.1 microM for compound 2, and 8.7 +/- 4.0 for 5-FU. The cytotoxic activity of 1 and 2 was reduced in the presence of the antioxidants N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and Mn(III) Tetrakis(1-methyl-4-pyridyl) porphyrin pentachloride (MnTMPyP), therefore suggesting that reactive oxygen species generation participates in the cytotoxic activity of these dihydrochalcones. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Planta medica, 2008, 74(3):312-313. | | Investigation on Anti-inflammatory Effect and Chemical Constituents of Total Flavonoid Aglycones from Tibetan Medicine Oxytropisfalcata.[Reference: WebLink] | Oxytropis falcata is a wild growing Leguminosae plant which distributes Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China. The herb of this plant has been known as one of “Three Anti-inflammatory Drugs” in Chinese Tibetan medicine, and used to treat inflammation and nociception for thousands years[1,2].
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In order to make the active material foundation corresponding to its anti-inflammatory effect clear, several main ingredients including essential oil, alkaloids, flavonoid aglycones and saponins were isolated, respectively, and then anti-inflammatory effect was evaluated and compared by TPA-induced ear oedema and carrageenan-induced peritonitis in mice. Subsequently, column chromatographic method was used to separate chemical constituents from the most active anti-inflammatory ingredient, whose structures were elucidated by NMR spectral data and physical and chemical properties. Oral administration of total flavonoid aglycones (1200 mg dry raw material/kg) could significantly (p < 0.01, compare to vehicle) inhibit the ear oedema induced by TPA and peritoneal leukocyte migration in mice at a rate of 61.1% and 56.4%, and indomethacin (10 mg/kg) showed 58.6% and 60.1% inhibition, respectively. Furthermore, pinostrobin, pinocembrin, 7-hydroxy flavonone, liquiritigenin, 2',4'-Dihydroxydihydrochalcone, 2ʹ,4ʹ-dihydroxy chalcone, 2ʹ-methoxy-4ʹ-hydroxy chalcone, 2ʹ-hydroxy-4ʹ-methoxy chalcone, 2ʹ,4-dihydroxy-4ʹ-methoxy chalcone, isoliquiritigenin, 3ʹ,7-dihydroxy-2ʹ,4ʹ-dimethoxy isoflavane, genistein, Ψ-baptigenin, formononetin, 7-hydroxy flavone, kaempferol, isorhamnetin, quercetin, myricetin, chrysin, apigenin, luteolin were isolated and elucidated from active ingredient.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results suggested that the total flavonoid aglycones possess most strong anti-inflammatory activity of main ingredients from Oxytropis falcata, and 12 flavonoids were isolated from which for the first time. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)