| Planta Med. 2000 Jun;66(5):483-4. |
| Cytotoxic triterpene acids from the Peruvian medicinal plant Polylepis racemosa.[Pubmed: 10909276] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Cytotoxicity-guided fractionation of the bark and stem extract of Polylepis racemosa led to the identification of ursolic acid, pomolic acid, 3-O-acetylpomolic acid, and 2-Oxopomolic acid. Pomolic acid was the most cytotoxic component, and was specific for M-14 melanoma and ME180 cervical carcinoma, with GI50 values of 6.9 and 8.3 micrograms/mL respectively. |
| Chem Biodivers. 2005 Jul;2(7):953-8. |
| Radical-scavenging activities of new hydroxylated ursane triterpenes from cv. Annurca apples.[Pubmed: 17193186] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
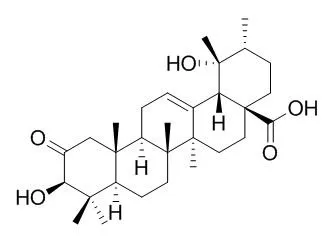
Two new ursolic acid triterpene derivatives, compounds 2 and 3, have been isolated from cv. Annurca apple fruit, a high-quality apple variety widely cultivated in southern Italy, together with the known 2-Oxopomolic acid (1). The new compounds were identified by means of different spectroscopic techniques as 3-epi-2-Oxopomolic acid (= (3alpha)-3,19-dihydroxy-2-oxours-12-en-28-oic acid; 2) and (1alpha)-1-hydroxy-3-oxours-12-en-28-oic acid (3). Compounds 1-3 were tested for their radical-scavenging activities with the aid of a 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay (Fig. 2).
CONCLUSIONS:
All three constituents showed activities similar to that of the reference antioxidant alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E). |
| Nat Prod Res. 2013;27(23):2219-23. |
| Triterpenoids from Fragaria ananassa calyx and their inhibitory effects on melanogenesis in B16-F10 mouse melanoma cells.[Pubmed: 23772756 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Column chromatographic technology was applied to isolate six purified ursane triterpenoids from the calyx of Fragaria ananassa and they were identified on the basis of spectroscopic methods to be ursolic acid (1), pomolic acid (2), 2-Oxopomolic acid (3), 3-O-acetyl pomolic acid (4), fupenzic acid (5) and euscaphic acid (6).
This is the first study in which these compounds have been isolated from the calyx of F. ananassa.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compared to a well-known inhibitor, α-arbutin, compounds 2-6 showed a significant decrease in intracellular melanin content in B16-F10 cells, and in culture media melanin. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)