| In vitro: |
| J Nat Prod. 2016 Mar 25;79(3):470-6. | | Antistaphylococcal Prenylated Acylphoroglucinol and Xanthones from Kielmeyera variabilis.[Pubmed: 26900954] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bioactivity-guided fractionation of the EtOH extract of the branches of Kielmeyera variabilis led to the isolation of a new acylphoroglucinol (1), which was active against all the MRSA strains tested herein, with pronounced activity against strain EMRSA-16. Compound 1 displayed an MIC of 0.5 mg/L as compared with an MIC of 128 mg/L for the control antibiotic norfloxacin. The structure of the new compound was elucidated by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic analysis and mass spectrometry, and experimental and calculated ECD were used to determine the absolute configurations. The compounds β-sitosterol (2), stigmasterol (3), ergost-5-en-3-ol (4), and osajaxanthone (5) also occurred in the n-hexane fraction.
CONCLUSIONS:
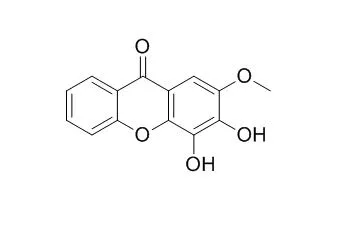
The EtOAc fraction contained nine known xanthones: 3,6-dihydroxy-1,4,8-trimethoxyxanthone (6), 3,5-dihydroxy-4-methoxyxanthone (7), 3,4-dihydroxy-6,8-dimethoxyxanthone (8), 3,4-Dihydroxy-2-methoxyxanthone (9), 5-hydroxy-1,3-dimethoxyxanthone (10), 4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone (11), kielcorin (12), 3-hydroxy-2-methoxyxanthone (13), and 2-hydroxy-1-methoxyxanthone (14), which showed moderate to low activity against the tested MRSA strains. | | Pharm Res. 1995 Nov;12(11):1756-60. | | Hepatoprotective activity of xanthones and xanthonolignoids against tert-butylhydroperoxide-induced toxicity in isolated rat hepatocytes--comparison with silybin.[Pubmed: 8592682] | Synthesize and evaluate the protective activity against tertbutylhydroperoxide-induced toxicity in freshly isolated rat hepatocytes of trans-kielcorin, trans-isokielcorin B, as well as their respective building blocks 3,4-Dihydroxy-2-methoxyxanthone and 2,3-dihydroxy-4-methoxyxanthone.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Wistar rats, weighing 200-250g were used. Hepatocyte isolation was performed by collagenase perfusion. Incubations were performed at 37 degrees C, using 1 million cells per milliliter in modified Krebs--Henseleit buffer. The protective activity was evaluated by measuring reduced and oxidized glutathione, lipid peroxidation and cell viability after inducing toxicity with tert-butylhydroperoxide (1.0 mM, 30 min), with or without the studied compounds in the concentrations of 0.025, 0.050, 0.100 and 0.200 mM. Silybin was tested in the same experimental conditions to serve as a positive control. Using these concentrations, the tested compounds prevented tert-butylhydroperoxide-induced lipid peroxidation and cell death in freshly isolated rat hepatocytes. All compounds were also effective in preventing perturbation of cell glutathione homeostasis in some extent. 3,4-Dihydroxy-2-methoxyxanthone and 2,3-dihydroxy-4-methoxyxanthone were more effective than trans-kielcorin and trans-isokielcorin B respectively. Silybin was less effective in protecting cells against lipid peroxidation and loss of cell viability than the four xanthonic derivatives.
CONCLUSIONS:
The tested compounds protected the freshly isolated rat hepatocytes against tert-butylhydroperoxide-induced toxicity. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)