METHODS AND RESULTS:
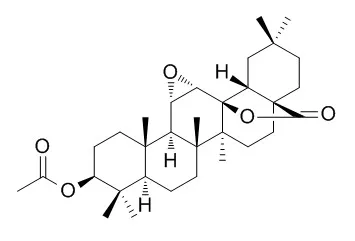
The methanolic extracts from branches (BEP) and leaves (LEP) of Eysenhardtia platycarpa significantly decreased the blood glucose levels in normal and streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. One new flavone, (1"R)-5,4',1"-trihydroxy-6,7-(3",3"-dimethylchroman)flavone (1), together with the known compounds 5,7-dihydroxy-6-methyl-8-prenylflavanone (3), 5,7-dihydroxy-8-methyl-6-prenylflavanone (4), 5,7-dihydroxy-6-prenylflavanone (5), 5,7-dihydroxy-8-prenylflavanone (6), 3-O-acetyloleanolic acid (7), oleanolic acid, 3beta-Acetoxy-11alpha,12alpha-epoxyoleanan-28,13beta-olide, lupeol, betulinic acid, beta-sitosterol, beta-sitosteryl beta-D-glucopyranoside, beta-sitosteryl palmitate, and 3-O-methyl-myo-inositol were isolated from BEP. Additionally, one new flavanone, (2S)-4'-O-methyl-6-methyl-8-prenylnaringenin (2), as well as the known compounds 3, 4, 6, 4'-O-methyl-8-prenylnaringenin (8), and 5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-8-prenylflavanone (9) were isolated from LEP.
CONCLUSIONS:
3-O-Acetyloleanolic acid (7), identified as the major constituent of BEP, showed a significant decrease (31 mg/kg of body weight, P < 0.05) in the glucose level of STZ-induced diabetic rats. The obtained results correlate with the traditional use of this species. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)