| Cell Research: |
| BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jan 2;14:1. | | Effects of eleutheroside B and eleutheroside E on activity of cytochrome P450 in rat liver microsomes.[Pubmed: 24383621] | Chemicals of herbal products may cause unexpected toxicity or adverse effect by the potential for alteration of the activity of CYP450 when co-administered with other drugs. Eleutherococcus senticosus (ES), has been widely used as a traditional herbal medicine and popular herbal dietary supplements, and often co-administered with many other drugs. The main bioactive constituents of ES were considered to be eleutherosides including eleutheroside B (EB) and Eleutheroside E (EE). This study was to investigate the effects of EB and EE on CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4 in rat liver microsomes in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Probe drugs of tolbutamide (TB), dextromethorphan (DM), chlorzoxazone (CLZ) and testosterone (TS) as well as eleutherosides of different concentrations were added to incubation systems of rat liver microsomes in vitro. After incubation, validated HPLC methods were used to quantify relevant metabolites.
The results suggested that EB and EE exhibited weak inhibition against the activity of CYP2C9 and CYP2E1, but no effects on CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 activity. The IC50 values for EB and EE were calculated to be 193.20 μM and 188.36 μM for CYP2E1, 595.66 μM and 261.82 μM for CYP2C9, respectively. Kinetic analysis showed that inhibitions of CYP2E1 by EB and EE were best fit to mixed-type with Ki value of 183.95 μM and 171.63 μM, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that EB and EE may inhibit the metabolism of drugs metabolized via CYP2C9 and CYP2E1, and have the potential to increase the toxicity of the drugs. |
|
| Animal Research: |
| Inflammation. 2014 Oct;37(5):1533-43. | | Eleutheroside E ameliorates arthritis severity in collagen-induced arthritis mice model by suppressing inflammatory cytokine release.[Pubmed: 24917466] | Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common arthritis and is mainly characterized by symmetric polyarticular joint disorders. Eleutheroside E (EE), a principal active constituent of Acanthopanax senticosus, is reported to have anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting NF-κB activities. However, the effects of EE on rheumatoid arthritis (RA) severity are largely unknown.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The purpose of this study was to indicate whether EE could ameliorate arthritis and reduce inflammatory cytokine release in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice. The results showed that EE attenuated the severity of arthritis by reducing the mean arthritis score and arthritis incidence. EE also significantly decreased the inflammatory cell infiltration, pannus formation, cartilage damage, and bone erosion of CIA mice. Furthermore, EE caused a marked decrease of the production of TNF-α and IL-6 in vivo and in vitro.
CONCLUSIONS:
These observations identify a novel function of EE that results in inhibition of cytokine release, highlighting EE was a potential therapeutic agent for RA. |
|
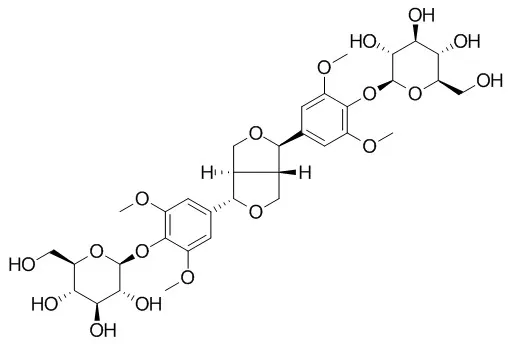
| Structure Identification: |
| Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Nov;38(11):1921-5. | | Utilization of circular dichroism experiment to distinguish acanthoside D and eleutheroside E.[Pubmed: 25802110 ] | Two lignan glycosides, acanthoside D (1) (=liriodendrin, (+)-syringaresinol di-O-β-D-glucopyranoside) and Eleutheroside E (2) have been confused each other for so long time, and hard to be distinguished each other.
Now, this two compounds need to be defined properly so that all the commercial mistakes and confusions should not be made.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
They have identical planar structures except for the configurations at C-7 and C-8 in each structure according to the chemistry database, SciFinder(®). The systematic name of acanthoside D is [(1S,3aR,4S,6aR)-tetrahydro-1H,3H-furo[3,4-c]furan-1,4-diyl]bis(2,6-dimethoxy-4,1-phenylene) bis-β-D-glucopyranoside (1), and the name of Eleutheroside E is [(1R,3aR,4S,6aS)-tetrahydro-1H,3H-furo[3,4-c]furan-1,4-diyl]bis(2,6-dimethoxy-4,1-phenylene) bis-β-D-glucopyranoside (2). The differences at two chiral centers do not make any differences in the NMR spectra. Thus, the circular dichroism were utilized to dissolve this difficult problem.
CONCLUSIONS:
Acanthoside D (1) showed a positive Cotton effect at 200 nm, whereas Eleutheroside E (2) exhibited a negative cotton effect at 200 nm. The absolute structure of acanthoside D was also confirmed by X-ray crystallography. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)