| In vivo: |
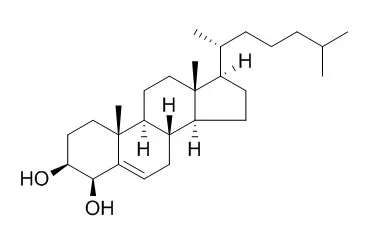
| J Biol Chem. 2002 Aug 30;277(35):31534-40. | | Metabolism of 4 beta -hydroxycholesterol in humans.[Pubmed: 12077124] | One of the major oxysterols in the human circulation is 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol formed from cholesterol by the drug-metabolizing enzyme cytochrome P450 3A4.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Deuterium-labeled 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol was injected into two healthy volunteers, and the apparent half-life was found to be 64 and 60 h, respectively. We have determined earlier the half-lives for 7 alpha-, 27-, and 24-hydroxycholesterol to be approximately 0.5, 0.75, and 14 h, respectively. Patients treated with certain antiepileptic drugs have up to 20-fold increased plasma concentrations of 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol. The apparent half-life of deuterium-labeled 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol in such a patient was found to be 52 h, suggesting that the high plasma concentration was because of increased synthesis rather than impaired clearance. 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol was converted into acidic products at a much slower rate than 7 alpha-hydroxycholesterol in primary human hepatocytes, and 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol was 7 alpha-hydroxylated at a slower rate than cholesterol by recombinant human CYP7A1. CYP7B1 and CYP39A1 had no activity toward 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that the high plasma concentration of 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol is because of its exceptionally slow elimination, probably in part because of the low rate of 7 alpha-hydroxylation of the steroid. The findings are discussed in relation to a potential role of 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol as a ligand for the nuclear receptor LXR. | | J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 19;276(42):38685-9. | | Antiepileptic drugs increase plasma levels of 4beta-hydroxycholesterol in humans: evidence for involvement of cytochrome p450 3A4.[Pubmed: 11514559 ] | The major cholesterol oxidation products in the human circulation are 27-hydroxycholesterol, 24-hydroxycholesterol, and 7alpha-hydroxycholesterol. These oxysterols are formed from cholesterol by specific cytochrome P450 enzymes, CYP27, CYP46, and CYP7A, respectively. An additional oxysterol present in concentrations comparable with 7alpha- and 24-hydroxycholesterol is 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We now report that patients treated with the antiepileptic drugs phenobarbital, carbamazepine, or phenytoin have highly elevated levels of plasma 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol. When patients with uncomplicated cholesterol gallstone disease were treated with ursodeoxycholic acid, plasma 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol increased by 45%. Ursodeoxycholic acid, as well as the antiepileptic drugs, are known to induce cytochrome P450 3A. Recombinant CYP3A4 was shown to convert cholesterol to 4beta-hydroxycholesterol, whereas no conversion was observed with CYP1A2, CYP2C9, or CYP2B6. The concentration of 4-alpha-hydroxycholesterol in plasma was lower than the concentration of 4beta-hydroxycholesterol and not affected by treatment with the antiepileptic drugs or ursodeoxycholic acid.
CONCLUSIONS:
Together, these data suggest that 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol in human circulation is formed by a cytochrome P450 enzyme. | | Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008 Mar;18(3):201-8. | | 4Beta-hydroxycholesterol is a new endogenous CYP3A marker: relationship to CYP3A5 genotype, quinine 3-hydroxylation and sex in Koreans, Swedes and Tanzanians.[Pubmed: 18300941] | To study the potential endogenous marker of CYP3A activity, 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol, and its relation to sex and the CYP3A5 geno/haplotypes and compare with CYP3A4/5 catalyzed 3-hydroxylation of quinine in the three major races.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The plasma concentration of 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol was measured in healthy Tanzanians (n=138), Swedes (n=161) and Koreans (n=149) by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The metabolic ratio of quinine/3-hydroxyquinine in plasma 16-h post dose was determined by high performance liquid chromatography, previously reported in Tanzanians and Swedes, and now also in Koreans. The participants were genotyped for relevant alleles of CYP3A5. Clear differences in the activity of both CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 were shown in the three major human races. Both 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol and quinine/3-hydroxyquinine metabolic ratio showed a higher CYP3A activity in women than in men.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results give strong evidence that the plasma concentration of 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol may be used as an endogenous marker of CYP3A activity (CYP3A4+5). |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)