| Structure Identification: |
| Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1990 Sep;38(9):2498-502. | | Isolation of two new coumarin glycosides from Notopterygium forbesii and evaluation of a Chinese crude drug, qiang-huo, the underground parts of N. incisum and N. forbesii, by high-performance liquid chromatography.[Pubmed: 2285981] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
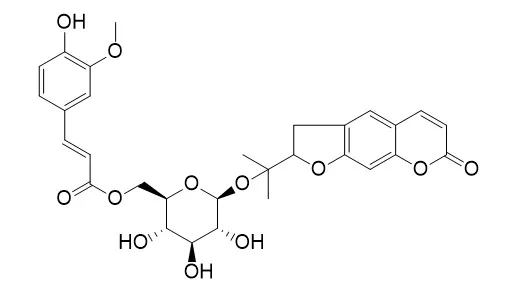
From the ether extract of the underground part of Notopterygium forbesii, two new coumarin glycosides, bergaptol-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside and 6'-O-trans-feruloylnodakenin(6'-Feruloylnodakenin), were isolated along with known compounds including seven furanocoumarins, two dihydrofuranocoumarins, a sterol glucoside and two phenolic compounds. Analysis of their contents by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) revealed that the underground part of N. forbesii contained large amounts of p-hydroxphenethyl anisate (0.7%), bergaptol glucoside (0.2%), nodakenin (2%) and 6'-O-trans-feruloylnodakenin (0.7%) and a lesser amount of notopterol (0.08%), while that of N. incisum contained a large amount of notopterol (1.2%) and less amounts of the others.
CONCLUSIONS:
The characteristic difference in chemical composition between the two species enabled us to identify the respective botanical sources of a Chinese crude drug, Qiang-huo derived from N. incisum and N. forbesii by HPLC. | | Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2009. | | Absorption and transportation characteristic of dihydrofurocoumarins from Rhizome et Radix Notopterygii in a model of Caco-2 cell monolayers.[Reference: WebLink] | To study the absorption and transportation characteristic of nodakenetin (NANI), nodakenin (ND), decuroside V (DEV), and forbesoside [6′-O-(trans-feruloyl)-nodakenin, 6'-Feruloylnodakenin FDE] isolated from Rhizome et Radix Notopterygii, which were classified four linear dihydrofurocouma-rins, in human intestinal epithelium.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Caco-2 (the human colon adenocarcinoma cell lines) cell monolayers were used as an intestinal epithelial cell model. The permeability of the four coumarins from apical side (AP side) to basolateral side (BL side) or from BL side to AP side was evaluated. The concentration of the four coumarins was measured by HPLC coupled with UV detector. Transportation parameters and permeability coefficients (Papp) were then calculated, and Papp values were compared with the reported values for model compounds, propranolol, and atenolol. The Papp values of NANI in the bi-directional transportation were quantitative degree of 1×106cm/s, which laid between propranolol often used as a control substance for high permeability and Atenolol often used as a control substance for poor permeability. Whereas Papp values of ND, DEV, and FDE were quantitative degree of 1×107cm/s, which was comparable with the Papp values of atenolol. The absorption and transportation of four coumarins were positive correlation to the concentration of 25-400 μmol/L.
CONCLUSIONS:
Four linear dihydrofurocoumarins can be absorbed across intestinal epithelial cells by passive diffusion mechanism. The NANI is moderately, while ND, DEV, and FDE are poorly absorbed compounds. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)