METHODS AND RESULTS:
A methanol extract from Pogostemon cablin showed a suppressive effect on umu gene expression of SOS response in Salmonella typhimurium TA1535/pSK1002 against the mutagen 2-(2-furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-furyl)acrylamide (furylfuramide).
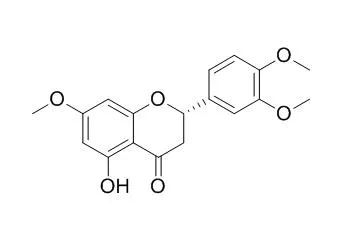
The methanol extract was re-extracted with hexane, dichloromethane, butanol, and water. A dichloromethane fraction showed a suppressive effect. Suppressive compounds against furylfuramide in the dichloromethane fraction were isolated by SiO(2) column chromatography and identified as 7,4'-di-O-methyleriodictyol (1), 7,3',4'-Tri-O-methyleriodictyol (2), and 3,7,4'-tri-O-methylkaempferol (3). In addition, three flavonoids, ombuine (4), pachypodol (5), and kumatakenin (6), were isolated and identified from the dichrolomethane fraction. Compounds 1 and 3 suppressed >50% of the SOS-inducing activity at <0.6 micromol/mL, and the ID(50) values of both compounds were 0.25 micromol/mL. Compound 2 showed a weakly suppressive effect (17%) at a concentration of 0.6 micromol/mL, and compounds 4-6 did not. These compounds were also assayed with 3-amino-1,4-dimethyl-5H-pyrido[4,3-b]indole (Trp-P-1), which requires liver metabolizing enzymes. Compounds 3-6 suppressed >80% of the SOS-inducing activity of Trp-P-1 at <0.06 micromol/mL, and compounds 1 and 2 suppressed 87 and 63% at a concentration of 0.3 micromol/mL.
In addition, these compounds were assayed with activated Trp-P-1, and the suppressed effects of these compounds were further decreased when compared to Trp-P-1.
CONCLUSIONS:
The antimutagenic activities of these compounds against furylfuramide, Trp-P-1, and activated Trp-P-1 were assayed by the Ames test using S. typhimurium TA100. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)