| In vitro: |
| J. Nat. Prod., 2016, 79(2):387-94. | | Diterpenes from the Trunk of Abies holophylla and Their Potential Neuroprotective and Anti-inflammatory Activities[Pubmed: 26812172 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
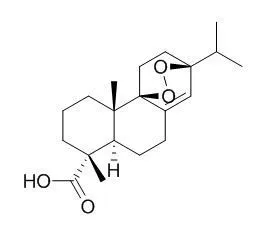
The 17 known compounds isolated were identified as abiesadine C (12),7-oxo-13β-hydroxyabiet-8(14)-en-18-oic acid (13), 7-oxo-13β-methoxyabiet-8(14)-en-18-oic acid (14),9,13β-epidioxy-8(14)-abieten-18-oic acid (9,13-Epidioxy-8(14)-abieten-18-oic acid,15),levopimaric acid endoperoxide (16), 15-hydroxy-8α,14α,12α,13α-diepoxyabietan-18-oic acid (17),12-oxo-8-hydroxyabiet- 13(14)-enoic acid (18),dehydroabietic acid (19),15-hydroxydehydroabietic acid (20), 7α-hydroxydehydroabietic acid (21), 7β-hydroxydehydroabietic acid (22),7-oxodehydroabietic acid (23),15-hydroxy-7-oxo-8,11,13-abietatrien-18-oic acid (24), (−)-8,11,13-abietatrien-7α-ol (25),7α,18-dihydroxydehydroabietanol (26), 8,11,13-abietatriene-15,18-diol 18-acetate (27),and abiesadine F (28),by comparison with NMR and MS data in the literature.The effects of the isolated compounds (1−28) on NO levels in LPS-stimulated murine microglia BV2 cells were evaluated.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 4, 15, and 18 exhibited moderate activities, with IC50values of 30.1 ± 6.5, 57.3 ± 0.2, and 56.1 ± 3.3 μM,respectively, without significant cell toxicity at 20 μM. The other compounds showed weak or no activity. L-NMMA was used as the positive control (IC50=24.8 ± 4.6 μM). | | J Plant Physiol. 2009 Mar 1;166(4):442-6. | | An allelopathic substance in red pine needles (Pinus densiflora).[Pubmed: 18755523 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Aqueous methanol extracts of red pine (Pinus densiflora) needles inhibited the growth of roots and shoots of cress (Lepidium sativum), lettuce (Lactuca sativa), alfalfa (Medicago sativa), ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum), timothy (Pheleum pratense), Digitaria sanguinalis and Echinochloa crus-galli. Increasing the extract concentration increased inhibition, suggesting that the pine needles may have growth inhibitory substances and possess allelopathic potential. The aqueous methanol extract of the pine needles was purified, and a main inhibitory substance was isolated and determined by spectral data as 9alpha,13beta-epidioxyabeit-8(14)en-18-oic acid(9,13-Epidioxy-8(14)-abieten-18-oic acid). This substance inhibited root and shoot growth of cress and Echinochloa crus-galli seedlings at concentrations greater than 0.1 mM. The endogenous concentration of the substance was 0.13 mmol/kg pine needle.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that 9alpha,13beta-epidioxyabeit-8(14)en-18-oic acid(9,13-Epidioxy-8(14)-abieten-18-oic acid) may contribute to the growth inhibitory effect of the pine needles and may play an important role in the allelopathy of red pine. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)