| Cell Research: |
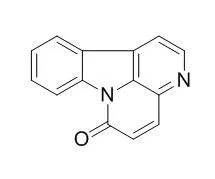
| J Nat Prod. 2014 Nov 26;77(11):2481-7. | | Canthin-6-one displays antiproliferative activity and causes accumulation of cancer cells in the G2/M phase.[Pubmed: 25379743] | Canthinones are natural substances with a wide range of biological activities, including antipyretic, antiparasitic, and antimicrobial. Antiproliferative and/or cytotoxic effects of canthinones on cancer cells have also been described, although their mechanism of action remains ill defined.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To gain better insight into this mechanism, the antiproliferative effect of a commercially available Canthin-6-one (1) was examined dose-dependently on six cancer cell lines (human prostate, PC-3; human colon, HT-29; human lymphocyte, Jurkat; human cervix, HeLa; rat glioma, C6; and mouse embryonic fibroblasts, NIH-3T3). Cytotoxic effects of 1 were investigated on the same cancer cell lines by procaspase-3 cleavage and on normal human skin fibroblasts. Strong antiproliferative effects of the compound were observed in all cell lines, whereas cytotoxic effects were very dependent on cell type. A better definition of the mechanism of action of 1 was obtained on PC-3 cells, by showing that it decreases BrdU incorporation into DNA by 60% to 80% and mitotic spindle formation by 70% and that it causes a 2-fold accumulation of cells in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle.
CONCLUSIONS:
Together, the data suggest that the primary effect of Canthin-6-one (1) is antiproliferative, possibly by interfering with the G2/M transition. Proapoptotic effects might result from this disturbance of the cell cycle. | | Nat Prod Commun. 2010 Jan;5(1):17-22. | | Canthin-6-one alkaloids and a tirucallanoid from Eurycoma longifolia and their cytotoxic activity against a human HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cell line.[Pubmed: 20184012] | Phytochemical investigation of the stems of Eurycoma longifolia Jack led to the isolation of two new Canthin-6-one alkaloids, 4,9-dimethoxyCanthin-6-one (1) and 10-hydroxy-11-methoxyCanthin-6-one (2), and a new tirucallane-type triterpenoid, 23,24,25-trihydroxytirucall-7-en-3,6-dione (3), along with 37 known compounds. Among these, an oxasqualenoid (4) was isolated as a natural product for the first time. The structures of the isolates were elucidated by spectroscopic and mass spectrometric means.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
All the isolates were evaluated for their cytotoxic activity against a HT-1080 human fibrosarcoma cell line. Among them, 9,10-dimethoxyCanthin-6-one (14, IC50 = 5.0 microM), 10-hydroxy-9-methoxyCanthin-6-one (15, IC50 = 7.2 microM), dihydroniloticin (18, IC50 = 8.2 microM), and 14-deacetyleurylene (34, IC50 = 3.2 microM) displayed stronger activity than the positive control 5-FU (IC50 = 9.2 microM). |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)