| Kinase Assay: |
| Chemico Biological Interactions, 2015, 226:49-57. | | Neuropharmacological effects of carvacryl acetate on δ-aminolevulinic dehydratase, Na+, K+-ATPase activities and amino acids levels in mice hippocampus after seizures.[Reference: WebLink] | Epileptic syndromes are highly prevalent neurological conditions and can often be disabling. In order to find an alternative for treatment, this study evaluated anticonvulsant effects of Carvacryl acetate (CA), a derivative of monoterpene carvacrol, after seizures induced by pilocarpine (P400), picrotoxin (PIC) or pentylenetetrazol (PTZ).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We also analyzed the CA effects on Na+, K+-ATPase and δ-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (δ-ALA-D) activities in hippocampus mice after seizures induced by P400, PIC or PTZ. In addition, glutamate, δ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamine and aspartate levels in mice hippocampus treated with CA after seizures induced by P400, PIC or PTZ were also measured. CA produced anticonvulsant effects against seizures induced by P400, PIC or PTZ, and its effects were reversed by flumazenil, suggesting that action mechanism can be mediated by GABAergic system. CA increased GABA levels, but did not alter glutamate and aspartate concentrations in mice hippocampus after seizures induced by P400, PIC or PTZ when compared with seizures induced by P400, PIC or PTZ (p < 0.05), respectively, as well as decreased glutamine content in mice hippocampus after seizures induced by PIC when compared with seizures induced by PIC (p < 0.05). In addition, CA also increased Na+, K+-ATPase and δ-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase activities after seizures induced by P400, PIC or PTZ when compared with seizures induced by P400, PIC or PTZ (p < 0.05), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study demonstrated that CA could be a future therapeutic option for treatment of epilepsy, with a multifactorial brain action mechanism. | | Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmacology, 2017,69(12):1773-1785. | | Carvacryl acetate, a novel semisynthetic monoterpene ester, binds to the TRPA1 receptor and is effective in attenuating irinotecan-induced intestinal mucositis in mice.[Reference: WebLink] | We aimed to determine whether Carvacryl acetate acts as a TRPA1 receptor agonist and its effects against irinotecan (CPT-11) induced intestinal mucositis in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
TRPA1 structure was obtained from a protein databank, and the 3D structure of Carvacryl acetate was determined. Appropriate binding conformations were discovered via automatic docking simulations. To determine the effect of Carvacryl acetate in vivo, mice were treated with either DMSO 2%, CPT-11, Carvacryl acetate followed by CPT-11, or HC-030031, a TRPA1 antagonist, followed by Carvacryl acetate. Jejunum samples were taken and structural, inflammatory and antioxidant parameters were studied.Eight amino acids residues in TRPA1 established stable interactions with Carvacryl acetate, which led to pharmacological efficacy against CPT-11-induced intestinal mucositis via reduction of both neutropenia and bacteremia, increase in villi height and crypt depth, decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1β, keratinocyte chemoattractant and tumour necrosis factor-α) and decrease in malondialdehyde and nitric oxide metabolite levels in the jejunum.
CONCLUSIONS:
Carvacryl acetate is a promising anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agent, a fact confirmed through observations of its interactions with TRPA1 in CPT-11-induced intestinal mucositis in mice. |
|
| Animal Research: |
| Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior,2013,112:42-48 | | Anxiolytic-like effects of carvacryl acetate, a derivative of carvacrol, in mice.[Reference: WebLink] | Studies showing anxiolytic-like properties of natural products have grown. This paper evaluated if Carvacryl acetate (CA) could be studied as an alternative drug to treat anxiety disorders.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Elevated plus maze (EPM) tests , light-dark box (LDB) tests, and marble-burying tests (MBTs) were performed on mice. In the first protocol, the anxiolytic-like activities of CA 25, 50, 75 and 100mg/kg at single doses were compared to those of the vehicle, buspirone 5mg/kg (BUSP) and diazepam 1mg/kg (DZP). In the second protocol, the anxiolytic-like actions of CA were tested for GABAergic and serotonergic systems. The time spent in the open arms (TSOA) and the number of open arms entries (NOAE) were measured in EPM; the time spent in the light box (TSLB) and the number of entries to light box (NELB) were measured in LDB; and the number of marbles buried (NMB) were measured in MBT. CA increased TSOA and NOAE in the EPM, as well as TSLB and NELB in the LDB and the NMB in the MBT. The anxiolytic-like activity of CA 25; 50; 75 and 100mg/kg was not associated with psychomotor retardation in the open field test and in the Rota rod test, contrarily with what happened with DZP. In the second protocol, to suggest the mechanism of action of CA, flumazenil 25mg/kg ip (FLU) and WAY 100,635 10mg/kg ip (WAY-5-HT1A antagonist) were also used. FLU+CA100 reduced TSOA in the EPM when compared to CA100 but WAY+CA100 did not. In LDB, FLU+CA100 reduced the TSLB when compared to CA100 but WAY+CA100 did not. In the MBT, FLU+CA100 inhibited the effect of CA100 on the NMB but WAY+CA100 did not.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, CA seems to have an anxiolytic-like effect, probably due to GABAergic agonist action, without psychomotor side effects. |
|


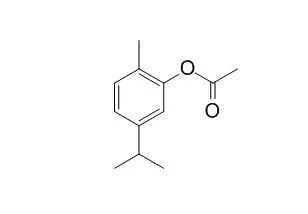



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)