| Animal Research: |
| Latin American Journal of Pharmacy; 2012 vol. 31, no. 3 | | Protective Activities of Cistanoside A on CCl4 Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
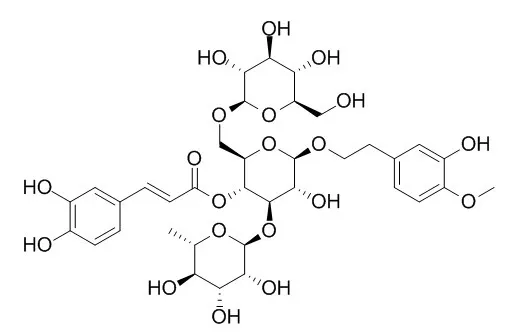
To evaluate the protective efficacy of Cistanoside A (C.A), a phenylethanol glycoside isolated from Cistanche deserticola, on CCl4 induced hepatotoxicity in mice, 50 animals were divided into five different protocols, and hepatic functional index were detected by diagnostic kits.To confirm the effect of Cistanoside A on free radical, tests on the free radical scavenging activities were also carried out in vitro. We found treatment with Cistanoside A (10, 20 mg/kg o.p. for 7 days) could significantly ameliorated the levels of hepatic function indices (AST, ALT, ALP and LDH) (P < 0.05). The biochemical results were also confirmed by histopathological examination. Cistanoside A treatment decreased the ballooning degeneration, moderated the hepatocytes apoptosis, and alleviated centrilobular and bridging necrosis which were observed in the CCl4 control group. Following experiments revealed that Cistanoside A could increase the activities of mitochondrial antioxidant enzymes (GST, SOD, and CAT) and respiratory marker enzymes (MDH, SDH, NADH dehydrogenase, and cytochrome c oxidases) (P < 0.05). In vitro, Cistanoside A exhibited strong scavenging activities for DPPH radical and superoxide anion radical.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results revealed that Cistanoside A possess protective activities on CCl4 induced hepatotoxicity in mice, which was involved with increasing free radicals clearing activities, alleviating lipid-overoxidation damage, and improving respiratory chain function in mitochondria. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)