| In vitro: |
| Bangladesh Journal of Pharmacology, 2014, 9(3):398-405. | | Antiviral activity of leaf-bud gum-resin of Tarenna asiatica.[Reference: WebLink] | The leaf-bud exudate of Tarenna asiatica (Rubiaceae: Ixoroideae, Pavetteae) is investigated for its biological activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The crude benzene extract and Corymbosin (pure compound isolated) were screened for antiviral activity by using ELISA and PCR methods against animal (blue tongue and chikungunya) and plant (papaya ring spot, sesbania mosaic and common bean mosaic) viruses. Both Corymbosin and benzene extract showed significant antiviral activity though Corymbosin was found relatively more potent against the animal and plant viruses tested.
CONCLUSIONS:
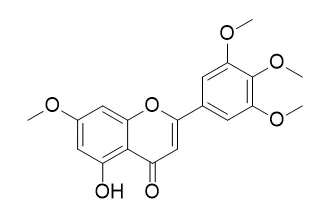
This is the first report of antiviral activity for the gumresin of T. asiatica, so also for the compound Corymbosin, against the plant viruses. | | Pharmaceutical Biology, 2003, 41(7):483-6. | | Antifungal Flavonoids from Ballota glandulosissima.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The flavonoids kumatakenin (1), pachypodol (2), 5-hydroxy-7,3′,4′-trimethoxyflavone (3), velutin (4), salvigenin (5), retusin (6) and Corymbosin (7) have been isolated from the aerial parts of Ballota glandulosissima Hub.-Mor & Patzak. Among them, 2–4 and 7 have not been reported previously in the genus Ballota.
CONCLUSIONS:
The antibacterial and antifungal activities of 1–4 and 6 were tested against Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus faecalis, Echerichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans, Candida krusei and Candida galabrata. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)