| In vitro: |
| Scand J Immunol. 2012 Aug;76(2):131-40. | | Induction of immune-related gene expression in Ctenopharyngodon idella kidney cells by secondary metabolites from immunostimulatory Alcaligenes faecalis FY-3.[Pubmed: 22606987 ] | This study was undertaken to isolate active secondary metabolites from immunostimulatory Alcaligenes faecalis FY-3 and evaluate their activities using grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella kidney (CIK) cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
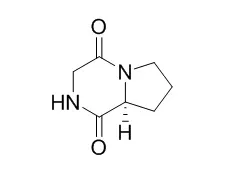
By applying chromatography techniques and successive recrystallization, three purified metabolites were obtained and identified by spectral data (mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance) as: (1) phenylacetic acid, (2) p-hydroxyphenylacetylamide and (3) Cyclo(Gly-L-Pro). CIK cells were stimulated by different concentrations (1, 10 and 100 μg/ml) of the isolated compounds, and expression of MyD88, IL-1β, TNF-α, type I-IFN and IL-8 genes at different time points (2, 8 and 24 h) post-stimulation was quantified by real-time PCR. The known immunostimulatory agent lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used as a positive control. To analyse whether these compounds are toxic to the cells, the methyl tetrazolium assay was employed to measure changes in cell viability. The obtained results revealed that transcribing level of MyD88, an important adaptor molecule in toll-like receptor signalling pathway, was augmented remarkably by all the three isolated compounds and LPS as early as 2-h exposure. These compounds also induced gene expression of cytokines such as IL-1β, TNF-α and type I-IFN. Under the experimental conditions, none of the test compounds is toxic to the CIK cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings demonstrate that the immunostimulatory properties of the three metabolites [phenylacetic acid, p-hydroxyphenylacetylamide and Cyclo(Gly-L-Pro) ] from A. faecalis FY-3 in CIK cells and highlight the potential of using these metabolites as immunostimulants in fish aquaculture. | | Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Dec 15;25(24):5756-61. | | Attenuation of TNF-α secretion by L-proline-based cyclic dipeptides produced by culture broth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.[Pubmed: 26546220 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To identify small molecule inhibitors of TNF-α, bioassay- and LC-MS-guided chemical investigation on EtOAc extract of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ABS-36 culture broth (EEPA) was performed, which yielded four proline-based cyclic dipeptides, Cyclo(Gly-L-Pro) (1), cyclo(l-Pro-l-Phe) (2), cyclo(trans-4-hydroxy-l-Pro-l-Phe) (3) and cyclo(trans-4-hydroxy-l-Pro-l-Leu) (4). Compounds 1 and 3 exhibited potent inhibition of TNF-α release with IC50 values of 4.5 and 14.2μg/mL, respectively, while EEPA showed IC50 of 38.8μg/mL under lipopolysaccharide treated RAW 264.7 cell ELISA assay. Also, marked attenuation of mRNA-expression of TNF-α was shown by all compounds. In vivo testing in rats of EEPA and chemically synthesized 4 validated significant TNF-α reduction with 51% (500mg/kg) and 79% (50mg/kg), respectively. In addition, all compounds exhibited significant diminution of IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA-expression levels and NO production.
CONCLUSIONS:
All samples displayed only weak toxicity to lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)