| Structure Identification: |
| Chemistry. 2015 Jun 8;21(24):8946-50. | | Generating skeletal diversity from the c19 -diterpenoid alkaloid deltaline: a ring-distortion approach.[Pubmed: 25950550] | The development of new drugs calls for large collections of diverse molecules with considerable complexity. Ring distortion of natural products provides an efficient and facile approach to access new architectures with intriguing biological activities, by harnessing their inherent complexity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
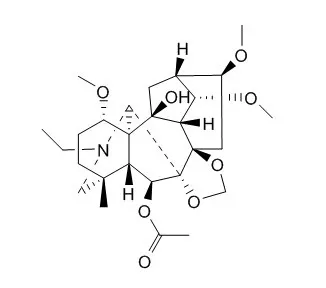
In this study, such a strategy has been explored on an abundant C19 -diterpenoid alkaloid, Deltaline, enabling the synthesis of 32 new derivatives bearing a broad spectrum of unique scaffolds. Extensive spectroscopic studies including X-ray crystallographic analyses strongly supported the structures of the obtained novel skeletons, which present comparable opportunities with the great contributions made by nature for discovery of new lead compounds. | | Nat Prod Commun. 2012 Jun;7(6):721-4. | | Unusual reactions of a 7,17-seco-type C19-diterpenoid alkaloid derived from deltaline.[Pubmed: 22816291] | | Treatment of a 7,17-seco-type C19-diterpenoid alkaloid (3), prepared from Deltaline (8), with triethylamine in either DMF or TEG (triethylene glycol) at 120 degrees C provided two interesting compounds 6 and 7. The structures of compounds 3, 6, and 7 were established based on extensive interpretations of their 1D and 2D NMR data. Compound 6, a lycoctonine-type C19-diterpenoid alkaloid, can be transformed from alkaloid 3 via Grob fragmentation, Prins reaction, and intramolecular disproportionation. The mechanism of the formation of compound 6 was confirmed by deuteration experiments. Product 7 was formed through a pinacol-like rearrangement of alkaloid 3. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)