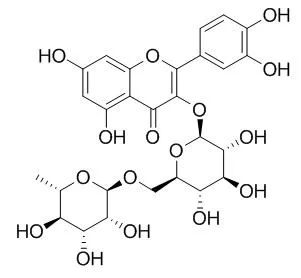
| Description: |
Rutin has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, gastroprotective, anticonvulsant, anti-angiogenic and antiviral properties, it may protect against spatial memory impairment induced by trimethyltin. Rutin exerts anti-inflammatory effects in UVB-irradiated mouse skin by inhibiting expression of COX-2 and iNOS, which is attributable to its suppression of p38 MAP kinase and JNK signaling responsible for AP-1 activation. |
| In vitro: |
| Food Chem., 2006, 98(3):508-12. | | Rutin content in buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) food materials and products[Reference: WebLink] | The Rutin content of buckwheat products was compared to the Rutin content in their raw materials, in order to evaluate their value for producing functional foods.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
There is much less Rutin in noodles (78 mg/kg, d.w.b. – dry weight basis), than in the dark buckwheat flour (218 mg/kg, d.w.b.) from which they are produced. One of the possible explanations is the presence of the Rutin degrading enzyme. In raw (uncooked) groats there is 230 mg/kg (d.w.b.) of Rutin and in precooked groats, 88 mg/kg (d.w.b.). In buckwheat beer and vinegar there is a negligible content of Rutin.
CONCLUSIONS:
Buckwheat leaf flour contains about 2700 mg/kg (d.w.b.) Rutin, and is thus a suitable material for enriching functional foods, giving it the potential for preventive nutrition. | | Arch Physiol Biochem . 2018 Oct;124(4):367-377. | | Rutin hydrate ameliorates cadmium chloride-induced spatial memory loss and neural apoptosis in rats by enhancing levels of acetylcholine, inhibiting JNK and ERK1/2 activation and activating mTOR signalling[Pubmed: 29214892] | | This study aimed at studying the potential neuroprotective effect of Rutin hydrate (RH) alone or in conjugation with α-tocopherol against cadmium chloride (CdCl2)-induced neurotoxicity and cognitive impairment in rats and to investigate the mechanisms of action. Rats intoxicated with CdCl2 were treated with the vehicle, RH, α-tocopherol or combined treatment were examined, and compared to control rats received vehicle or individual doses of either drug. Data confirmed that RH improves spatial memory function by increasing acetylcholine availability, boosting endogenous antioxidant potential, activating cell survival and inhibiting apoptotic pathways, an effect that is more effective when RH was conjugated with α-tocopherol. Mechanism of RH action includes activation of PP2A mediated inhibiting of ERK1/2 and JNK apoptotic pathways and inhibition of PTEN mediated activation of mTOR survival pathway. In conclusion, RH affords a potent neuroprotection against CdCl2-induced brain damage and memory dysfunction and co-administration of α-tocopherol enhances its activity. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014 Oct 1;559:38-45. | | Rutin inhibits UVB radiation-induced expression of COX-2 and iNOS in hairless mouse skin: p38 MAP kinase and JNK as potential targets.[Pubmed: 24875145] | Exposure to ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation, a complete environmental carcinogen, induces oxidative and inflammatory skin damage, thereby increasing the risk of skin carcinogenesis. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of a wide variety of plant polyphenols have been reported. Rutin (3-rhamnosyl-glucosylquercetin), a polyphenol present in many edible plants, possesses diverse pharmacological properties including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimutagenic and anticancer activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study was aimed to investigate the effects of Rutin on UVB-induced inflammation in mouse skin in vivo. Topical application of Rutin onto the dorsal skin of female HR-1 hairless mice 30 min prior to UVB irradiation diminished epidermal hyperplasia and the levels of proteins modified by 4-hydroxynonenal, which is a biochemical hallmark of lipid peroxidation. Topical application of Rutin also significantly inhibited UVB-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), two representative inflammatory enzymes, in hairless mouse skin. Rutin inhibited the DNA binding of activator protein-1 (AP-1) and phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) in mouse skin exposed to UVB. Moreover, Rutin attenuated UVB-induced phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase and c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK). Pharmacological inhibition of p38 MAP kinase and JNK decreased UVB-induced expression of COX-2 in mouse skin.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these findings suggest that Rutin exerts anti-inflammatory effects in UVB-irradiated mouse skin by inhibiting expression of COX-2 and iNOS, which is attributable to its suppression of p38 MAP kinase and JNK signaling responsible for AP-1 activation. | | Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Oct 3;54:50-8. | | Effect of quercetin and rutin in some acute seizure models in mice.[Pubmed: 24857758] | Quercetin is one of the most widely occurring flavonoid which is also often present in plants as glycosidic form - Rutin. These compounds are ingredients of plant diet and are also present in numerous pharmaceutical preparations and diet supplements which are taken by patients suffering from epilepsy and treating with antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Influence of these compounds on central nervous system-related effects was proved both in experimental and clinical studies. Their influence on anxiety, depression, memory processes and convulsant activity was reported.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of quercetin and Rutin in some models of seizures, i.e., in the model of psychomotor seizures induced by 6Hz stimulation, in the maximal electroshock seizure threshold and intravenous pentylenetetrazole tests in mice. We also examined a possible mechanism of anticonvulsant activity of quercetin and its influence on action of two AEDs, i.e., valproic acid and levetiracetam, in the 6Hz seizure test. Our results revealed only a weak anticonvulsant potential of the studied flavonoids because they showed anticonvulsant action at doses from 10 to 200mg/kg only in the 6Hz test and did not change seizure thresholds in the remaining tests. Moreover, anticonvulsant action of the studied flavonoids was short-term, noted only at pretreatment time ranging between 30 and 60min. The highest anticonvulsant activity of quercetin was correlated with its high plasma and brain concentration, which was revealed in a pharmacokinetic study. We did not note changes in the anticonvulsant action of the used AEDs combined with quercetin in the model of psychomotor seizures in mice. Neither quercetin and Rutin nor combinations of quercetin with the studied AEDs produced any significant impairments of motor coordination (assessed in the chimney test), muscular strength (investigated in the grip-strength test) and long-term memory (evaluated in the passive avoidance test) in mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results of the present study suggest that quercetin and Rutin have only weak and short-term anticonvulsant potential. These flavonoids seem to be safe for patients with epilepsy because they neither changed activity of the studied AEDs nor produced any adverse effects. | | Brain Res. 2009 Oct 6;1292:123-35. | | Rutin protects the neural damage induced by transient focal ischemia in rats.[Pubmed: 19631195] | Free radical induced neural damage is implicated in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury and antioxidants are reported to have neuroprotective activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study was designed to assess the neuroprotective role of Rutin (Vitamin P), and mechanism of action. The middle cerebral artery (MCA) of an adult male Wistar rat was occluded for 2 h and reperfused for 22 h. The administration of Rutin (25 mg/kg bwt., orally) once daily for 21 days before middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) showed marked reduction in infarct size, reduced the neurological deficits in terms of behaviors, suppressed neuronal loss and diminished the p53 expression in MCAO rats. A significantly depleted activity of antioxidant enzymes, glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GR), catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) and content of glutathione (GSH) in MCAO group were protected significantly in MCAO group pretreated with Rutin. Conversely, the elevated level of thiobarbituric acid reactive species (TBARS), H(2)O(2) and protein carbonyl (PC) in MCAO group was attenuated significantly in Rutin-pretreated group when compared with MCAO group.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Rutin attenuates ischemic neural apoptosis by reducing the expression of p53, preventing morphological changes and increasing endogenous antioxidant enzymatic activities. Thus, Rutin treatment may represent a novel approach in lowering the risk or improving the function of ischemia-reperfusion brain injury-related disorders. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)