| In vitro: |
| Neoplasma. 2015;62(3):419-31. | | Deltonin induced both apoptosis and autophagy in head and neck squamous carcinoma FaDu cell.[Pubmed: 25866222 ] | For decades, despite the advancement of medical science, the prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), has not improved. Deltonin is one of the major active components of Dioscorea Zingiberensis Wright that has been used for anthrax, rheumatic heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis etc.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
By employing HNSCC FaDu cell and normal human epidermal keratinocyte, we investigate Deltonin efficacy and associated mechanism in both cell culture and nude mice xenografts. Deltonin treatment selectively prevents proliferation of FaDu cells by cell-cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis, via activating checkpoint kinase Chk1and Chk2 as well as caspases 8, 9 and 3. Meanwhile, we found that treatment with Deltonin induced autophagy, which played a protective role against Deltonin-induced apoptosis. Further studies revealed that Deltonin activated autophagy by Akt-mTOR signaling. Additionally, xenograft model showed that administration of Deltonin significantly inhibited tumor growth and prolonged survival of tumor bearing mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our studies suggested that Deltonin might be a potential chemotherapeutic agent against HNSCC, which might contribute to clinical application and pharmacological study of Deltonin in future anti-cancer research. | | Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Oct;39(19):3782-7. | | Study on steroidal saponins from Dioscorea zingiberensis and their platelet aggregation activities.[Pubmed: 25612440] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
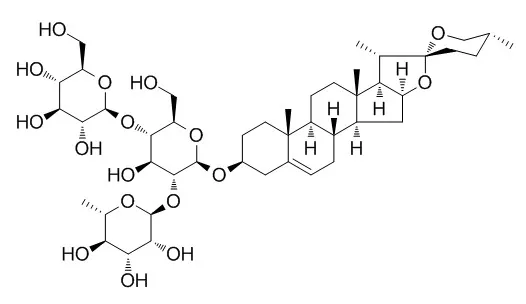
Using the absorbent resin, silica gel and ODS column chromatography as well as semi-preparative HPLC, ten compounds were isolated from 70% ethanol extract of tubers of Dioscorea zingiberensis C. H. Wright, and their structures were elucidated as trigoneoside XIIIa (1), parvifloside (2), trigoneoside IVa (3), deltoside (4), protobioside (5), lilioglycoside k (6), zingiberensis newsaponin I (7), Deltonin (8), prosapogenin A of dioscin (9), and trillin (10) on the basis of NMR and MS spectral data analysis. Among these compounds, 1, 3, 5 and 6 were isolated from this plant for the first time.
CONCLUSIONS:
In the screening test on platelet aggregation, compounds 7 and 8 exhibited induction effect on platelet aggregation, while compound 9 exhibited significant inhibitory effect on platelet aggregation in vitro. | | Steroids. 2015 Apr;96:30-6. | | Deltonin inhibits angiogenesis by regulating VEGFR2 and subsequent signaling pathways in endothelial cells.[Pubmed: 25554580] |
Deltonin is a steroidal saponin which could suppress tumor growth through suppressing angiogenesis, but the mechanisms have not been directly elucidated yet.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we showed that Deltonin inhibited the proliferation of primary cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in vitro; notably, it could significantly inhibit HUVECs migration, invasion, and tube formation, which are indispensable progresses of angiogenesis. We further demonstrated that Deltonin could inhibit VEGF-induced blood vessel formation in vivo. What is more, we found that Deltonin blocked VEGF triggered phosphorylation of key intracellular angiogenic molecules, such as VEGFR2, Src family kinase, focal adhesion kinase (FAK), extracellular signal-related kinase (Erk1/2) and AKT kinase, accompanied with the increase of phosphorylated P38MAPK.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the present study demonstrates that Deltonin inhibits angiogenesis through regulating VEGFR2 signaling pathway as well as AKT/MAPK signaling pathways in endothelial cells. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Fitoterapia. 2010 Dec;81(8):1147-56. | | Anti-thrombotic activity and chemical characterization of steroidal saponins from Dioscorea zingiberensis C.H. Wright.[Pubmed: 20659537 ] | Steroidal saponins have long attracted scientific attention, due to their structural diversity and significant biological activities. Total steroidal saponins (TSS) extracted from the rhizomes of Dioscorea zingiberensis C.H. Wright (DZW) constitute an effective treatment for cardiovascular disease. However, the active constituents contained in DZW rhizomes and their pharmacological properties are not fully understood. The aim of this work is to determine and quantify the active constituents in DZW rhizomes using fingerprint technique, and evaluate its anti-thrombotic activity using inferior vena cava ligation thrombosis rat model and pulmonary thrombosis mice model after being gavaged with TSS for 1 or 2weeks.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the study, a chemical fingerprint method was firstly established and validated to quantify and standardize TSS from DZW rhizomes including parvifloside, protoDeltonin, protodioscin, protogracillin, zingiberensis saponin, Deltonin, dioscin and trillin. TSS extracted from DZW rhizomes were showed to have the inhibitions on platelet aggregation (PAG) and thrombosis, and prolong activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), thrombin time (TT), and prothrombin time (PT) in a dose-dependent manner in rats. TSS also prolonged the bleeding time and clotting time in a dose-dependent manner in mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicate that TSS could inhibit thrombosis by both improving the anticoagulation activity and inhibiting PAG action, suggesting that TSS from DZW rhizomes have the potential to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases by anti-thrombotic action. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)