| In vitro: |
| Thromb Res. 1990 Jul 1;59(1):121-30. | | Inhibition of thrombin- and collagen-induced phosphoinositides breakdown in rabbit platelets by a PAF antagonist--denudatin B, an isomer of kadsurenone.[Pubmed: 2169076] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
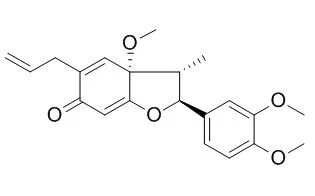
Denudatin B, an isomer of kadsurenone, was isolated from Magnolia fargesii. It inhibited the aggregation and ATP release of washed rabbit platelets caused by platelet-activating factor (PAF) in a concentration-dependent manner. The IC50 on PAF (2 ng/ml)-induced aggregation was about 10 micrograms/ml. High concentration of Denudatin B (greater than 50 micrograms/ml) also inhibited the aggregation and ATP release of platelets caused by ADP, collagen, arachidonic acid and thrombin. However, shape change of platelets still existed. Prolongation of the incubation time with platelets could not cause further inhibition, and the aggregability of platelets could be restored after Denudatin B was washed out from platelets. Thrombin-induced thromboxane B2 formation was almost completely suppressed. In the absence of extracellular calcium (EGTA 1 mM), ATP release caused by thrombin was inhibited. Thrombin-induced rise of the intracellular calcium concentration was suppressed by Denudatin B, but not by BN52021 or kadsurenone. The generation of inositol phosphate in washed platelets caused by collagen, PAF and thrombin was also suppressed.
CONCLUSIONS:
The data indicate that PAF antagonist Denudatin B has nonspecific antiplatelet action at high concentration by inhibiting phosphoinositides breakdown induced by collagen and thrombin. | | Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct 2;187(1):39-47. | | Vasorelaxing effect in rat thoracic aorta caused by denudatin B, isolated from the Chinese herb, magnolia fargesii.[Pubmed: 2176980] | Denudatin B is an antiplatelet agent isolated from the flower buds of Magnolia fargesii. We studied the effects of Denudatin B on the vasoconstriction of rat thoracic aorta induced by high potassium (K+) solution, norepinephrine (NE) and caffeine, and to elucidate its mode of action.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The contraction of rat aorta caused by high K+ (60 mM) and cumulative concentrations of CaCl2 (0.03-3 mM) was inhibited concentration dependently by Denudatin B with an IC50 of 21.2 micrograms/ml. NE (3 microM)-induced phasic and tonic contractions of rat aorta were inhibited by pretreatment with Denudatin B (10-100 micrograms/ml). The relaxing action of Denudatin B persisted in denuded aorta, in Ca2(+)-free and EGTA (2 mM)-containing medium. The vasorelaxing effects were not affected by indomethacin (20 microM), hemoglobin (10 microM) or methylene blue (50 microM) and were not accompanied by PGI2 formation. In quin-2/AM-loaded cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells, Denudatin B (100 micrograms/ml) inhibited the increase of intracellular calcium caused by NE (3 microM) in the presence or absence of extracellular calcium. Denudatin B did not affect the caffeine (10 mM)-induced contraction and the increase in intracellular calcium. Denudatin B (100 micrograms/ml) increased the cGMP, but not the cAMP level in intact and denuded aorta. The 45Ca2+ influx induced in rat aorta by high K+ (60 mM) or NE (3 microM) was markedly inhibited by Denudatin B in a concentration-dependent manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Denudatin B relaxed vascular smooth muscle by inhibiting the Ca2+ influx through voltage-gated and receptor-operated Ca2+ channels; its effect to increase cGMP may enhance the vasorelaxation. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)