| Kinase Assay: |
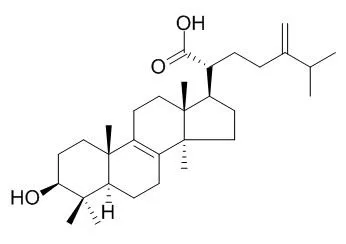
| J Tradit Complement Med. 2012 Oct;2(4):312-22. | | Eburicoic Acid, an Active Triterpenoid from the Fruiting Bodies of Basswood Cultivated Antrodia cinnamomea, Induces ER Stress-Mediated Autophagy in Human Hepatoma Cells.[Pubmed: 24716146] | Antrodia cinnamomea, a Taiwan-specific medicinal mushroom, can manipulate biological activities, including hepatoprotection, anti-inflammation, anti-hepatitis B virus activity, anticancer activity, etc.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, the anti-liver cancer activity and molecular mechanisms of Eburicoic acid, the second most abundant triterpenoid from the fruiting bodies of basswood cultivated Antrodia cinnamomea was investigated using the human hepatoma Hep 3B cells. The results show that Eburicoic acid effectively reduced Hep 3B cell viability within 24 hours, and the IC50 was 18.4 μM, which was equivalent to 8.7 μg/mL. Besides, Eburicoic acid induced conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II and a large number of autophagosomes/autolysosomes formation. In depth investigation for the molecular mechanisms, revealed that Eburicoic acid firstly promoted reactive oxygen species generation and ATP depletion, leading to endoplasmic reticulum stress, followed by elevated cytosolic calcium ion concentration and BiP expression, downregulated phosphorylation of DAPK, upregulated phosphorylation of Beclin-1, JNK, and Bcl-2, and finally induced autophagy in Hep 3B cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Eburicoic acid has significant anti-liver cancer effects and more distinctive mechanisms. |
|
| Animal Research: |
| Food Chem. 2013 Dec 1;141(3):3020-7. | | Hepatoprotective effects of eburicoic acid and dehydroeburicoic acid from Antrodia camphorata in a mouse model of acute hepatic injury.[Pubmed: 23871054] | The hepatoprotective effects of Eburicoic acid (TR1) and dehydroEburicoic acid (TR2) from Antrodia camphorata (AC) against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver damage were investigated in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Eburicoic acid and TR2 was administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) for 7 days prior to the administration of CCl4. Pretreatment with TR1 and TR2 prevented the elevation of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and liver lipid peroxides in CCl4-treated mice. The activities of antioxidant enzymes [catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx)], nitric oxide (NO) production, and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) were decreased after the treatment with TR1 and TR2 in CCl4-treated mice. Western blotting revealed that Eburicoic acid and TR2 significantly decreased inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expressions and increased the expression of cytochrome P4502E1 (CYP2E1) in CCl4-treated mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, we speculate that Eburicoic acid and TR2 protect the liver from CCl4-induced hepatic damage via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)