| In vitro: |
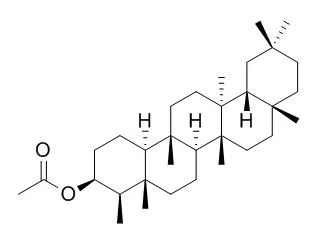
| Industrial Crops & Products, 2015, 74:752-8. | | Antifungal, antibacterial and anticancer activities of Ficus drupacea L. stem bark extract and biologically active isolated compounds[Reference: WebLink] | Seven biochemical compounds from stem bark extracts including β-amyrin (1), β-sitosterol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (2), 5-O-methyllatifolin (3), oleanolic acid (4), epifriedelanol (Epifriedelanol acetate,5), friedelin (6) and epilupeol acetate (7) were isolated and identified.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Of all the seven compounds, the compounds 3 and 7 exhibited the highest antifungal and antibacterial activities against screened microorganisms. Aspergillus versicolor and A. ochraceus were the most sensitive microorganisms to the isolated compounds whereas Candida albicans was the most resistant fungus. Compounds 4, 5, and 6 did not exhibit much variation in their antibacterial activities except against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. The most sensitive bacterium to isolated compounds was Bacillus cereus whereas the most resistant one was Enterobacter cloacae. However, compounds 4, 6 and 7 exhibited the highest antiproliferative activities against most cancer cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
The study reveal that F. drupacea stem barks contain several compounds that have antimicrobial activities against diverse human pathogenic, food and agricultural microbes as well as anticancer activities against human cancer cells of HeLa, MCF-7, Jurkat, HT-29 and T24. These results may guide the search for new natural products with chemotherapeutic attributes. | | Pak J Pharm Sci. 2013 Mar;26(2):245-50. | | Phenolic contents, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of Elaeocarpus floribundus Blume.[Pubmed: 23455191] | Elaeocarpus floribundus is higher plant that has been used as traditional medicine for treating several diseases. There is no previous report on phytochemicals and bioactivity studies of this species.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this investigation, triterpenoids friedelin, epifriedelanol(Epifriedelanol acetate) and β-sitosterol were isolated from its leaves and stem bark. Determination of total phenolic content of methanolic extract of leaves and stem bark was carried out using Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. All extracts and isolated compounds were subjected to screening of antioxidant activity using DPPH free radical scavenging method and cytotoxic activities by MTT assay towards human T4 lymphoblastoid (CEM-SS) and human cervical (HeLa) cancer cells. In the total phenolic content determination, methanolic extract of leaves gave higher value of 503.08±16.71 mg GAE/g DW than stem bark with value of 161.5±24.81 mg GAE/g DW. Polar extracts of leaves and stem bark possessed promising antioxidant activity with methanol extract of stem bark exhibited strongest activity with IC50 value of 7.36±0.01 μg/ml.
CONCLUSIONS:
In the cytotoxic activity assay, only chloroform extract of leaves showed significant activity with IC50 value of 25.6±0.06 μg/ml against CEM-SS cancer cell, while friedelin and epifriedelanol were found to be active against the two cancer cells with IC50 values ranging from 3.54 to 11.45 μg/ml. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)