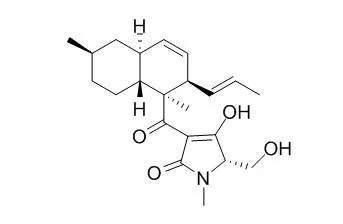
| Structure Identification: |
| Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Feb 1;268(2):659-66. | | The effect of equisetin on energy-linked reactions in Rhodospirillum rubrum chromatophores.[Pubmed: 2536535] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Light-induced proton uptake, light-induced carotenoid absorbance shift, photophosphorylation, and hydrolysis of Mg-ATP, Ca-ATP, and PPi in Rhodospirillum rubrum chromatophores are shown to be inhibited by the antibiotic Equisetin.
The Mg- and Ca-ATPase activities of purified F0F1-ATPase are inhibited by Equisetin. In contrast, only the Ca-ATPase activity of purified F1-ATPase is decreased by Equisetin, whereas the Mg-ATPase is stimulated. Both Equisetin and N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD) inhibit the hydrolytic activity of the purified H+-PPase but not the hydrolytic activity of soluble PPase from R. rubrum and yeast. The I50 for the PPi hydrolysis is near 20 microM for both Equisetin and DCCD. The action of Equisetin on membranes is compared to the effect of Triton X-100 and carbonyl cyanide p-trifluoromethoxyhydrazone.
CONCLUSIONS:
On the basis of these new data, Equisetin is proposed to act nonspecifically on membranes and hydrophobic domains of proteins. | | Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 May 1;460(2):210-5. | | A new enzyme involved in the control of the stereochemistry in the decalin formation during equisetin biosynthesis.[Pubmed: 25770422] | Tetramic acid containing a decalin ring such as Equisetin and phomasetin is one of the characteristic scaffolds found in fungal bioactive secondary metabolites.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Polyketide (PKS)-nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) hybrid enzyme is responsible for the synthesis of the polyketide scaffold conjugated with an amino acid. PKS-NRPS hybrid complex programs to create structural diversity in the polyketide backbone have begun to be investigated, yet mechanism of control of the stereochemistry in a decalin formation via a Diels-Alder cycloaddition remains uncertain.
CONCLUSIONS:
Here, we demonstrate that fsa2, which showed no homology to genes encoding proteins of known function, in the fsa cluster responsible for Equisetin and fusarisetin A biosynthesis in Fusarium sp. FN080326, is involved in the control of stereochemistry in decalin formation via a Diels-Alder reaction in the Equisetin biosynthetic pathway. | | Chemistry. 2013 Sep 23;19(39):13040-6. | | Biomimetic synthesis of equisetin and (+)-fusarisetin A.[Pubmed: 24038394] | (+)-Fusarisetin A belongs to a group of acyl tetramic acid natural products that show potential anticancer activity. Equisetin, a biogenetically related acyl tetramic acid, contains the basic skeleton of (+)-fusarisetin A.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We proposed that Equisetin and (+)-fusarisetin A share a biosynthetic pathway that starts with naturally occurring (S)-serine and an unsaturated fatty acid. In support of this hypothesis, we have demonstrated that a cyclization sequence involving an intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction followed by a Dieckmann cyclization of polyenoylamino acid yielded Equisetin. The aerobic oxidation of Equisetin, promoted by either Mn(III)/O2 or a reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced by visible-light chemistry, gave peroxyfusarisetin, which could be easily reduced to (+)-fusarisetin A.
CONCLUSIONS:
We report herein detailed information on the biogenetic synthesis of Equisetin and (+)-fusarisetin A. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)