| Structure Identification: |
| Acta pharmaceutica sinica, 1984. | | STUDIES ON THE ACTIVE PRINCIPLES OF THE CHINESE DRUG "SHANG LU" (PHYTOLACCA ESCULENTA VAN HO UTTE)Ⅱ. THE ISOLATION AND STRUCTURE OF ESCULENTOSIDE E AND F.[Reference: WebLink] | In a previous paper we reported the isolation of esculentoside A, B, C and D from Phytolacca eseulenta Van Houtte.In pharmacological experiments the total saponins and esculentoside A exerted considerable enhancement of phagocytic function of leucocytes and promoted DNA synthesis in mice. .
METHODS AND RESULTS:
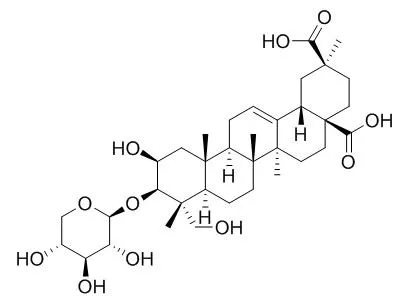
In further search for active principles, four kinds of crystals (Ⅰ), (Ⅱ), (Ⅲ) and (Ⅳ) were isolated from the 0.01 M pH 7.3 phosphate buffer extract of the plant by silica gel column chromatography. On the basis of chemical properties and spectral data (NMR, ~(13)CNMR, UV, IR, Ms spectra), crystal (Ⅰ) was shown to be 2-hydroxyl esculentic acid, i.e. jaligonic acid which has been considered to have good antiinflammatory action; crystal (Ⅱ) was found to be 3-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl-2-hydroxylesculentic acid and was named as esculentosid E which is identical to phytolaccoside G from Phytolacca americana. Crystal (Ⅲ) is 3-O(β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-xylopyranosyl)_(1→4)-2-hydroxyl esculentic acid named as esculentoside F.
CONCLUSIONS:
Esculentoside E was first obtained from this plant and esculentoside F so far has not been reported in literature. Because of the scanty sample of crystal (Ⅳ), its structure is still under investigation. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)