| Cell Research: |
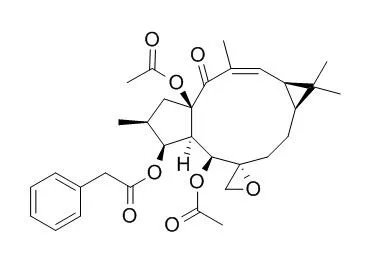
| Chinese Journal of Cancer Prevention & Treatment, 2014 , 21 (23) :1865-1870. | | Mechanism of euphorbiasteroid inducing apoptosis of HL-60 cells[Reference: WebLink] | To investigate the effect of Euphorbiasteroid on inducing the apoptosis of HL-60 cells and identify the role of Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathway in this process.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
HL-60 cells were treated with low, middleand high dose of Euphorbiasteroid in vitro for 24 h and after that cell counting Kit-8 was used to detect cell proliferation. The morphology of HL-60 cells was observed under light and fluorescent microscopy. The early cell apoptosis was detected using flow cytometry with Annexin V/PI double staining. The expressions of Bcl-2, Bax, Caspase-9, Caspase-3 mRNA were analyzed by RT-PCR. The activity of Caspase-9, 3 was examined by chromatometry, ELISA detect Caspase-9, Caspase-3 activity of protein. HL-60 cell proliferation was inhibited significantly by Euphorbiasteroid administration (F=42.97, P<0.001). Comparison between different concentrations, the difference was statistically significant, P<0.05. Early cell apoptosis rate of HL-60 cells was enhanced markedly after Euphorbiasteroid administration (F=56.74, P<0.001), after 10, 20, 40 μg/mL Euphorbiasteroid treatment for 24 h, the HL-60 cells early apoptosis rate respectively were(23.4±3.1)%, (35.7±4.3)%, (53.2±3.9)%, and cells presented typical apoptosis morphological changes. Bax mRNA transcription level increased significantly, the Bcl-2 mRNA transcription level decreased significantly (F=53.45, P<0.001) after Euphorbiasteroid administration in a dose-dependent manner. Caspase-9, Caspase-3 mRNA were up-regulated in the transcriptional level, and a compound dose dependent (F=34.21, P<0.001), semen euphorbiae sterol effect on the HL-60 cells after 24 h Caspase-9, 3 protein activity significantly increased (F=54.33, P<0.001), with the increase of concentration of semen euphorbiae sterol the protein activity increased.
CONCLUSIONS:
Euphorbiasteroid induces HL-60 cells to apoptosis via promoting Bcl-2/Bax apoptotic signaling pathway in a dose-dependent manner. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)