| In vitro: |
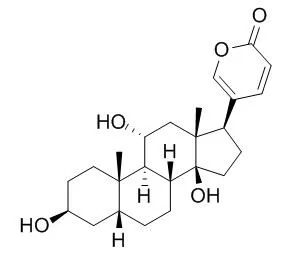
| Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 19;7(3):3533-47. | | Gamabufotalin, a major derivative of bufadienolide, inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis by suppressing VEGFR-2 signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 26657289 ] | Gamabufotalin (CS-6), a main active compound isolated from Chinese medicine Chansu, has been shown to strongly inhibit cancer cell growth and inflammatory response. However, its effects on angiogenesis have not been known yet.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we sought to determine the biological effects of CS-6 on signaling mechanisms during angiogenesis. Our present results fully demonstrate that CS-6 could significantly inhibit VEGF triggered HUVECs proliferation, migration, invasion and tubulogenesis in vitro and blocked vascularization in Matrigel plugs impregnated in C57/BL6 mice as well as reduced vessel density in human lung tumor xenograft implanted in nude mice. Computer simulations revealed that CS-6 interacted with the ATP-binding sites of VEGFR-2 using molecular docking. Furthermore, western blot analysis indicated that CS-6 inhibited VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 kinase and suppressed the activity of VEGFR-2-mediated signaling cascades.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, our studies demonstrated that CS-6 inhibited angiogenesis by inhibiting the activation of VEGFR-2 signaling pathways and CS-6 could be a potential candidate in angiogenesis-related disease therapy. | | Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 29;7(13):15725-37. | | Gamabufotalin triggers c-Myc degradation via induction of WWP2 in multiple myeloma cells.[Pubmed: 26894970 ] | Deciding appropriate therapy for multiple myeloma (MM) is challenging because of the occurrence of multiple chromosomal changes and the fatal nature of the disease.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the current study, Gamabufotalin (GBT) was isolated from toad venom, and its tumor-specific cytotoxicity was investigated in human MM cells. We found GBT inhibited cell growth and induced apoptosis with the IC50 values <50 nM. Mechanistic studies using functional approaches identified GBT as an inhibitor of c-Myc. Further analysis showed that GBT especially evoked the ubiquitination and degradation of c-Myc protein, thereby globally repressing the expression of c-Myc target genes. GBT treatment inhibited ERK and AKT signals, while stimulating the activation of JNK cascade. An E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, WWP2, was upregulated following JNK activation and played an important role in c-Myc ubiquitination and degradation through direct protein-protein interaction. The antitumor effect of GBT was validated in a xenograft mouse model and the suppression of MM-induced osteolysis was verified in a SCID-hu model in vivo.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our study identified the potential of GBT as a promising therapeutic agent in the treatment of MM. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)