| Kinase Assay: |
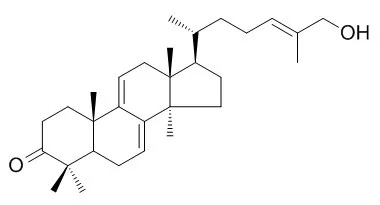
| Chem. Pharm. Bull., 1986, 34(7):3025-8. | | Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Triterpenes from Ganoderma lucidim[Reference: WebLink] | | The 70% MeOH extract of Ganoderma lucidum had an inhibitory effect on angiotensin converting enzyme activity, and from this extract, five new triterpenes, named ganoderal A, Ganoderol A and ganoderol B, and ganoderic acids K and S, were isolated. Their structures were determined on the basis of spectral evidence. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
| J Sep Sci. 2006 Nov;29(17):2609-15. | | Quality evaluation of Ganoderma through simultaneous determination of nine triterpenes and sterols using pressurized liquid extraction and high performance liquid chromatography.[Pubmed: 17313101] | A method combining HPLC and pressurized liquid extraction was developed for simultaneous quantification of nine components, including eight triterpenes (ganoderic acid A, ganoderic acid Y, ganoderic acid DM, Ganoderol A, ganoderol B, ganoderal A, methyl ganoderate D and ganoderate G) and a sterol (ergosterol), in Ganoderma.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The determination was achieved by using a Zorbax ODS C18 analytical column (4.6 x 250 mm id, 5 microm) and gradient elution with diode-array detection. All calibration curves showed good linearity (r2 > 0.9997) within the test ranges. The developed method showed good repeatability for the quantification of the nine investigated components in Ganoderma with intra- and inter-day variations of less than 2.4% and 4.1%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The validated method was successfully applied to quantify the nine components in two species of Ganoderma, i.e. G. lucidum and G. sinense, used as Lingzhi in China. Furthermore, hierarchical clustering analysis based on the nine components in HPLC profiles from the tested 11 samples showed that chemical characteristics were significantly different between G. lucidum and G. sinense, which suggested that clinical investigation should be performed so as to ensure the safety and efficacy of medication. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)