| In vitro: |
| Cell Biol Toxicol. 2017 Dec 6. | | Ginkgolide K promotes the clearance of A53T mutation alpha-synuclein in SH-SY5Y cells.[Pubmed: 29214369] | Alpha-synuclein (α-syn) is associated to Parkinson's disease (PD). The aggregated form of α-syn has potential neurotoxicity. Thus, the clearance of α-syn aggregation is a plausible strategy to delay disease progression of PD.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In our study, we found that the treatment of Ginkgolide B (GB) and Ginkgolide K (GK) reduced cell death, and enhanced cell proliferation in SH-SY5Y cells, which overexpressed A53T mutant α-syn. Surprisingly, GK, but not GB, promoted the clearance of A53T α-syn, which can be abolished by autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine, indicating that GK-induced autophagy intervened in the clearance of A53T α-syn. However, GK did not affect the NEDD4 that belongs to the ubiquitin ligase in the endosomal-lysosomal pathway. Furthermore, GK treatment inhibited the p-NF-kB/p65 and induced the PI3K, BDNF, and PSD-95.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, GK increased the clearance of α-syn, reduced cell death, and triggered complex crosstalk between different signaling pathways. Although our results show a potentially new therapeutic candidate for PD, the details of this mechanism need to be further identified. | | Neurotoxicology. 2012 Jan;33(1):59-69. | | Neuroprotective effect of ginkgolide K on glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in PC 12 cells via inhibition of ROS generation and Ca(2+) influx.[Pubmed: 22120026 ] | Glutamate is considered to be responsible for the pathogenesis of cerebral ischemia disease. [Ca(2+)](i) influx and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production are considered to be involved in glutamate-induced apoptosis process.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we investigated the neuroprotective effects of Ginkgolide K in the glutamate-induced rat's adrenal pheochromocytoma cell line (PC 12 cells) and the possible mechanism. Glutamate cytotoxicity in PC 12 cells was accompanied by an increment of malondialdehyde (MDA) content and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release, as well as Ca(2+) influx, bax/bcl-2 ratio, cytochrome c release, caspase-3 protein and ROS generation, and reduction of cell viability and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). Moreover, treatment with glutamate alone resulted in decrease activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX) activity. However, pretreatment with Ginkgolide K significantly reduced MDA content, LDH release, as well as Ca(2+) influx, cytochrome c release, bax/bcl-2 ratio, caspase-3 protein and ROS production, and attenuated the decrease of cells viability and MMP. In addition, Ginkgolide K remarkedly up-regulated SOD and GSH-PX activities.
CONCLUSIONS:
All these findings indicated that Ginkgolide K protected PC12 cells against glutamate-induced apoptosis by inhibiting Ca(2+) influx and ROS production. Therefore, the present study supports the notion that Ginkgolide K may be a promising neuroprotective agent for the treatment of cerebral ischemia disease. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Jun 8;833:221-229. | | Ginkgolide K promotes angiogenesis in a middle cerebral artery occlusion mouse model via activating JAK2/STAT3 pathway.[Pubmed: 29890157] | Ginkgolide K (GK) is a new compound extracted from the leaves of Ginkgo biloba, which has been recognized to exert anti-oxidative stress and neuroprotective effect on ischemic stroke. While whether it plays an enhanced effect on angiogenesis during ischemic stroke remains unknown.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of Ginkgolide K on promoting angiogenesis as well as the protective mechanism after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Using the transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) mouse model, we found that GK (3.5, 7.0, 14.0 mg/kg, i.p., bid., 2 weeks) attenuated neurological impairments, and promoted angiogenesis of injured ipsilateral cortex and striatum after 14 days of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in mice. Further, GK (3.5 mg/kg in vivo, 10 μM in vitro) significantly up-regulated the expressions of HIF-1α and VEGF in tMCAO mouse brains and in b End3 cells after OGD/R, and GK-induced upregulation of HIF-1α and VEGF in b End3 cells could be abolished by JAK2/STAT3 inhibitor AG490.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results demonstrate that GK promotes angiogenesis after ischemia stroke through increasing the expression of HIF-1α/VEGF via JAK2/STAT3 pathway, which provide an insight into the novel clinical application of GK and its analogs in ischemic stroke therapy in future. |
|


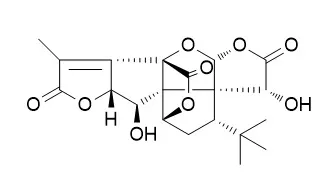



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)