| Description: |
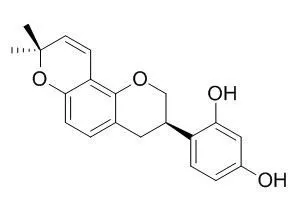
Glabridin is a GABAA receptor positive modulator promoting fatty acid oxidation and improving learning and memory, which has antioxidative,anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, estrogen receptor agonism, anti-metastasis, anti-melanogenesis and neuroprotective effects. Glabridin may possess a therapeutic effect on metabolic disorders( such as diabetes and hyperglycemia), by modulating glucose metabolism through AMPK in skeletal muscle cells.
|
| Targets: |
NOS | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | ERK | JNK | NF-kB | AMPK | Akt | GLUT | LDL | GABAA receptor |
| In vitro: |
| Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jun;171(12):3037-50. | | Glabridin inhibits migration and invasion by transcriptional inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase 9 through modulation of NF-κB and AP-1 activity in human liver cancer cells.[Pubmed: 24641665] | High mortality and morbidity rates for hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan primarily result from uncontrolled tumour metastasis. Glabridin, a prenylated isoflavonoid of licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra) roots, is associated with a wide range of biological properties, such as regulation of energy metabolism, oestrogenic, neuroprotective, anti-osteoporotic and skin whitening. However, the effect of Glabridin on the metastasis of tumour cells has not been clarified.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A wound healing model and Boyden chamber assays in vitro were used to determine the effects of Glabridin on the migration and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HHC) cells. Western blot analysis, gelatin zymography, real-time PCR and promoter assays were used to evaluate the inhibitory effects of Glabridin on matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) expression in these cells.
Glabridin significantly inhibited migration/invasion capacities of HCC cells, Huh7 and Sk-Hep-1, cell lines that have low cytotoxicity in vitro, even at high concentrations. Western blot analysis and gelatin zymography showed that Glabridin inhibited the expression, activities and protein levels of MMP9 and the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and JNK1/2. These inhibitory effects were associated with an up-regulation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and a down-regulation of the transcription factors NF-κB and activator protein 1 signalling pathways. Finally, the administration of Glabridin effectively suppressed the tumour formation in the hepatoma xenograft model in vivo.
CONCLUSIONS:
Glabridin inhibited the invasion of human HCC cells and may have potential as a chemopreventive agent against liver cancer metastasis. | | Parasitol Int. 2014 Apr;63(2):349-58. | | Glabridin induces oxidative stress mediated apoptosis like cell death of malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum.[Pubmed: 24361284] | Plants are known as the source of novel agents for developing new antimalarial drugs. Glabridin is a polyphenolic flavonoid, a main constituent in the roots of Glycyrrhiza glabra possesses various biological activities. However, its anti-plasmodial activity is unexplored.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present work, it is for the first time demonstrated that Glabridin inhibits Plasmodium falciparum growth in vitro with an IC50 23.9±0.43μM. Glabridin showed poor cytotoxicity in vitro with an IC50 246.6±0.88μM against Vero cell line and good selectivity index (9.6). In erythrocytic cycle, trophozoite stage was found to be most sensitive to Glabridin. In silico study showed that Glabridin inhibits Pf LDH enzyme activity by acting on NADH binding site. Glabridin induced oxidative stress by the generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Glabridin could induce apoptosis in parasite as evidenced by the depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm), activation of caspase like proteases and DNA fragmentation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Glabridin exhibits antiplasmodial activity and is suitable for developing antimalarial agent from a cheap and sustainable source. | | Environ Toxicol . 2018 Jun;33(6):679-685. | | Glabridin induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in oral cancer cells through the JNK1/2 signaling pathway[Pubmed: 29663662] | | Abstract
Glabridin, a flavonoid extracted from licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra), possesses various biological properties, including anticancer activities. However, the effect of Glabridin on oral cancer cell apoptosis and the underlying molecular mechanisms has not been elucidated. In this study, we demonstrated that Glabridin treatment significantly inhibits cell proliferation in human oral cancer SCC-9 and SAS cell lines. Flow cytometric assays demonstrated that Glabridin induced several features of apoptosis, such as sub-G1 phase cell increase and phosphatidylserine externalization. Furthermore, Glabridin induced apoptosis dose-dependently in SCC-9 cells through caspase-3, -8, and -9 activation and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage. Moreover, Glabridin increased the phosphorylation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase, p38, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathways in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, the inhibition of the JNK1/2 inhibitor significantly reversed the Glabridin-induced activation of the caspase pathway. In conclusion, our findings suggest that Glabridin induces oral cancer cell apoptosis through the JNK1/2 pathway and is a potential therapeutic agent for oral cancer.
Keywords: JNK1/2 pathway; apoptosis; caspase; Glabridin; oral cancer. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015 Mar 3. | | Glabridin, an isoflavan from licorice root, downregulates iNOS expression and activity under high-glucose stress and inflammation.[Pubmed: 25737160] | In females, hyperglycemia abolishes estrogen-vascular protection, leading to inflammation and oxidative stress that are related to diabetes-associated cardiovascular complications. Such knowledge led us to examine the potential of Glabridin, as a replacement of estrogen anti-inflammatory activity under high-glucose conditions.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In macrophage-like cells, chronic glucose stress (28 and 44 mM) upregulated inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mRNA expression by 42 and 189%, respectively. Pretreatment with Glabridin, under chronic glucose stress, downregulated the LPS-induced nitric oxide secretion and nitrotyrosine formation, by 39 and 21%, respectively. Pretreatment with estradiol did not prevent the LPS-induced nitrotyrosine formation. Furthermore, Glabridin, brought about a decrease in the LPS-induced iNOS mRNA expression by 48%, as compared to cells pretreated with estradiol. Glabridin decreased protein levels of liver iNOS by 69% in adult mouse offspring which developed hyperglycemia after early fetal exposure to a saturated fatty acid-enriched maternal diet. Glabridin also decreased liver nitrotyrosine levels in offspring of regular diet-fed mothers after further receiving high-fat diet.
CONCLUSIONS:
Such results indicate that Glabridin retains anti-inflammatory abilities to regulate the synthesis and activity of iNOS under high-glucose levels, implying that a Glabridin supplement may serve as an anti-inflammatory agent in diabetes-related vascular dysfunction. | | Cancer Res. 2000 Oct 15;60(20):5704-9. | | Estrogenic and antiproliferative properties of glabridin from licorice in human breast cancer cells.[Pubmed: 11059763] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
There is an increasing demand for natural compounds that improve women's health by mimicking the critical benefits of estrogen to the bones and the cardiovascular system but avoiding its deleterious effects on the breast and uterus. The estrogenic properties of Glabridin, the major isoflavan in licorice root, were tested in view of the resemblance of its structure and lipophilicity to those of estradiol. The results indicate that Glabridin is a phytoestrogen, binding to the human estrogen receptor and stimulating creatine kinase activity in rat uterus, epiphyseal cartilage, diaphyseal bone, aorta, and left ventricle of the heart. The stimulatory effects of 2.5-25 microg/animal Glabridin were similar to those of 5 microg/animal estradiol. Chemical modification of Glabridin showed that the position of the hydroxyl groups has a significant role in binding to the human estrogen receptor and in proliferation-inducing activity. Glabridin was found to be three to four times more active than 2'-O-methylGlabridin and 4'-O-methylGlabridin, and both derivatives were more active than 2',4'-O-methylGlabridin. The effect of increasing concentrations of Glabridin on the growth of breast tumor cells was biphasic. Glabridin showed an estrogen receptor-dependent, growth-promoting effect at low concentrations (10 nM-10 microM) and estrogen receptor-independent antiproliferative activity at concentrations of > 15 microM.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first study to indicate that isoflavans have estrogen-like activities. Glabridin and its derivatives exhibited varying degrees of estrogen receptor agonism in different tests and demonstrated growth-inhibitory actions on breast cancer cells. | | Inflammopharmacology . 2018 Apr;26(2):551-559. | | Downregulation of iNOS and elevation of cAMP mediate the anti-inflammatory effect of glabridin in rats with ulcerative colitis[Pubmed: 28707183] | | Abstract
Background: Alternative medicine is widely accepted by public and becoming an attractive approach for treatment of various diseases. Glabridin (Gla), a major flavonoid present in licorice root, was reported to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Objective: The study aimed to investigate the possible protective role of Gla against dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced ulcerative colitis (UC) in rats and to clarify the molecular mechanisms underlying Gla function.
Methods: Forty male Wistar rats were divided into control, colitis group (rats received 5% DSS in drinking water for 7 days), Gla group (50 mg/kg, orally, once daily), and sulfasalazine (SLZ) group (500 mg/kg, orally, once daily). Each of Gla and SLZ was administered 1 week ahead of DSS and parallel with its administration.
Results: Gla ameliorated the inflammatory alterations induced by DSS. Gla group showed a reduction in colon concentration of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and a decreased colon myeloperoxidase activity (MPO). Gla treatment downregulated inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) gene expression in rat colon with a decreased content of nitric oxide (NO). Gla also increased cyclic AMP (cAMP) concentration in rat colon compared to colitis group. Such findings were comparable to or even better than those obtained by SLZ treatment. The histological features of UC such as ulceration and inflammatory cell infiltrations were improved in rat group treated by Gla.
Conclusion: Gla proved a potent anti-inflammatory role in UC through different mechanisms and, being a natural product, it could be safely used as a protective measure in inflammatory bowel diseases.
Keywords: CAMP; Glabridin; INOS; Myleoperoxidase; TNF-α; Ulcerative colitis. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)