| Kinase Assay: |
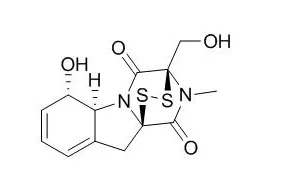
| MBio. 2016 Apr 5;7(2):e02242. | | Gliotoxin Suppresses Macrophage Immune Function by Subverting Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-Trisphosphate Homeostasis.[Pubmed: 27048806] | Aspergillus fumigatus, an opportunistic fungal pathogen, spreads in the environment by releasing numerous conidia that are capable of reaching the small alveolar airways of mammalian hosts. In otherwise healthy individuals, macrophages are responsible for rapidly phagocytosing and eliminating these conidia, effectively curbing their germination and consequent invasion of pulmonary tissue. However, under some circumstances, the fungus evades phagocyte-mediated immunity and persists in the respiratory tree.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we report thatA. fumigatusescapes macrophage recognition by strategically targeting phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate [PtdIns(3,4,5)P3] metabolism through Gliotoxin, a potent immunosuppressive mycotoxin. Time-lapse microscopy revealed that, in response to the toxin, macrophages cease to ruffle, undergo abrupt membrane retraction, and fail to phagocytose large targets effectively. Gliotoxin was found to prevent integrin activation and interfere with actin dynamics, both of which are instrumental for phagocytosis; similar effects were noted in immortalized and primary phagocytes. Detailed studies of the underlying molecular mechanisms of toxicity revealed that inhibition of phagocytosis is attributable to impaired accumulation of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3and the associated dysregulation of downstream effectors, including Rac and/or Cdc42.
CONCLUSIONS:
Strikingly, in response to the diacylglycerol mimetic phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, Gliotoxin-treated macrophages reactivate beta integrins, reestablish actin dynamics, and regain phagocytic capacity, despite the overt absence of plasmalemmal PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 Together, our findings identify phosphoinositide metabolism as a critical upstream target of Gliotoxin and also indicate that increased diacylglycerol levels can bypass the requirement for PtdIns(3,4,5)P3signaling during membrane ruffling and phagocytosis. | | Mar Drugs. 2015 Oct 2;13(10):6259-73. | | Gliotoxin Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells.[Pubmed: 26445050 ] | The discovery of new bioactive compounds from marine natural sources is very important in pharmacological research.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here we developed a Wnt responsive luciferase reporter assay to screen small molecule inhibitors of cancer associated constitutive Wnt signaling pathway. We identified that Gliotoxin (GTX) and some of its analogues, the secondary metabolites from marine fungus Neosartorya pseufofischeri, acted as inhibitors of the Wnt signaling pathway. In addition, we found that GTX downregulated the β-catenin levels in colorectal cancer cells with inactivating mutations of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) or activating mutations of β-catenin. Furthermore, we demonstrated that GTX induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in multiple colorectal cancer cell lines with mutations of the Wnt signaling pathway.
CONCLUSIONS:
Together, we illustrated a practical approach to identify small-molecule inhibitors of the Wnt signaling pathway and our study indicated that GTX has therapeutic potential for the prevention or treatment of Wnt dependent cancers and other Wnt related diseases.
|
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)