| In vitro: |
| Phytomedicine. 2011 Mar 15;18(5):425-30. | | Estrogenic activities of Psoralea corylifolia L. seed extracts and main constituents.[Pubmed: 21382704] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Estrogenic activities of ethanol extract and its active components from Psoralea corylifolia L. were studied using various in vitro assays. The main components from ethanol extract were analyzed to be bakuchiol, psoralen, isobavachalcone, Isobavachromene, and bavachinin. In a fractionation procedure, hexane and chloroform fractions showed estrogenic activity in yeast transactivation assay and E-screen assay. In yeast transactivation assay, ethanol extract, hexane, and chloroform fractions showed significantly higher activities at a concentration of 1.0 ng/ml, and bakuchiol at the concentration of 10(-6) M was showed the highest activity, especially, which was higher than genistein at the same concentration.
CONCLUSIONS:
In E-screen assay, cell proliferation of bakuchiol (10(-6) M) showed similar estrogenic activity with genistein (10(-6) M). In ER binding assay, bakuchiol displayed the strongest ER-binding affinity (IC(50) for ERα=1.01×10(-6) M, IC(50) for ERβ=1.20×10(-6) M) and bakuchiol showed five times higher affinity for ERα than for ERβ. | | Planta Med. 2008 Sep;74(11):1405-8. | | In vitro BACE-1 inhibitory phenolic components from the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia.[Pubmed: 18666047] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
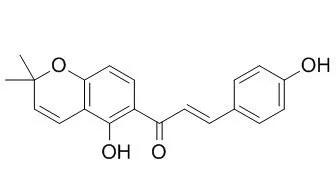
A new isoflavone, neocorylin ( 1) was isolated from the seeds extract of Psoralea corylifolia L. (Fabaceae), together with eight known constituents ( 2 - 9), i. e., bakuchiol ( 2), psoralen ( 3), bavachromene ( 4), Isobavachromene ( 5), bavachalcone ( 6), isobavachalcone ( 7), 7,8-dihydro-8-(4-hydrophenyl)-2,2-dimethyl-2 H,6 H-[1,2- B:5,4- B']dipyran-6-one ( 8), and bavachinin ( 9). The structure of the new isoflavone 1 was elucidated as 7-hydroxy-3-[2-methyl-2-(4-methylpenten-3-yl)-2 H-chromen-6-yl]-4 H-chromen-4-one by spectroscopic analyses.
CONCLUSIONS:
Neocorylin ( 1) as well as related compounds 2, 4 - 6, 8 and 9 exhibited a significant inhibitory effect on baculovirus-expressed BACE-1 in vitro. | | Dent Mater J . 2020 Aug 2;39(4):690-695. | | Inhibitory effects on Streptococcus mutans of antibacterial agents mixed with experimental fluoride varnish[Pubmed: 32522914] | | Abstract
We investigated the inhibitory effect of antibacterial agents mixed with experimental fluoride varnish (EFV) on Streptococcus mutans. The antibacterial agents used were (1 and 10) mM of xanthorrhizol, bakuchiol, bavachalcone, Isobavachromene, and bavachromene. Agar diffusion tests were performed on S. mutans (1.1×1010 CFU/mL), using antibacterial agents without and with EFV. Bavachalcone showed the highest inhibition zone without and with EFV at both (1 and 10) mM (p<0.05). All EFV with antibacterial agents showed greater inhibition and semi-inhibition zones than EFV alone (p<0.05). The cell viability of each antibacterial agent was not significantly different from the vehicle controls (p>0.05), except xanthorrhizol and bakuchiol at 1 mM. All antibacterial agents were effective, while antibacterial agents with EFV co-formulations were more effective than EFV alone. Bavachalcone was the most effective agent against S. mutans, indicating its potential usefulness with fluoride varnish in preventing dental caries.
Keywords: Antibacterial agent; Dental caries; Fluoride varnish; Streptococcus mutans. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)