| Structure Identification: |
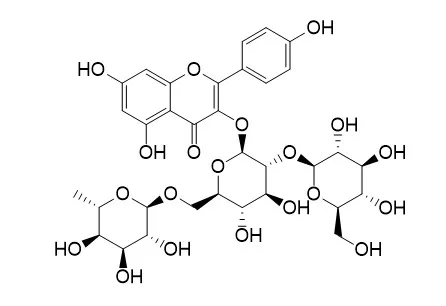
| Volume 67, Issue 1, 18 May 2009, Pages 31-37 | | Extraction and purification of flavanone glycosides and kaemferol glycosides from defatted Camellia oleifera seeds by salting-out using hydrophilic isopropanol[Reference: WebLink] | | The purpose of this research was to investigate a salting-out procedure for isolating four flavonoid glycosides from defatted Camellia oleifera seeds. The procedure included extraction with 80% methanol, methanol removal and addition of an equal amount of hydrophilic isopropanol and salt to separate the isopropanol fraction from the water layer. Using successive column chromatography, kaemferol-3-O-[2-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-6-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl]-β-d-glucopyranoside (compound 1), kaemferol-3-O-[2-O-β-d-xylopyranosyl-6-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl]-β-d-glucopyranoside (compound 2), naringenin-7-O-[β-d-xylopyranosyl(1 → 6)][β-d-glucopyranosyl(1 → 3)-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl(1 → 2)]-β-d-glucopyranoside (compound 3) and naringenin-7-O-β-d-xylopyranosyl(1 → 6)-β-d-glucopyranoside (compound 4) were obtained. The structure of compound 3, a new flavanone glycoside, was analyzed using UV, FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR and HR-FAB-MS. Quantification using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) demonstrated that defatted C. oleifera seed cake contains 7.92, 17.7, 2.23 and 1.06 mg/g of the four compounds. The extraction efficiencies of the four compounds were increased by 23.17%, 7.59%, 48.67% and 47.22% from those obtained with n-butanol partition extraction. This new extraction technique is simpler, faster and less expensive than the traditional extraction method. Accordingly, this salting-out method can potentially replace the existing one. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)